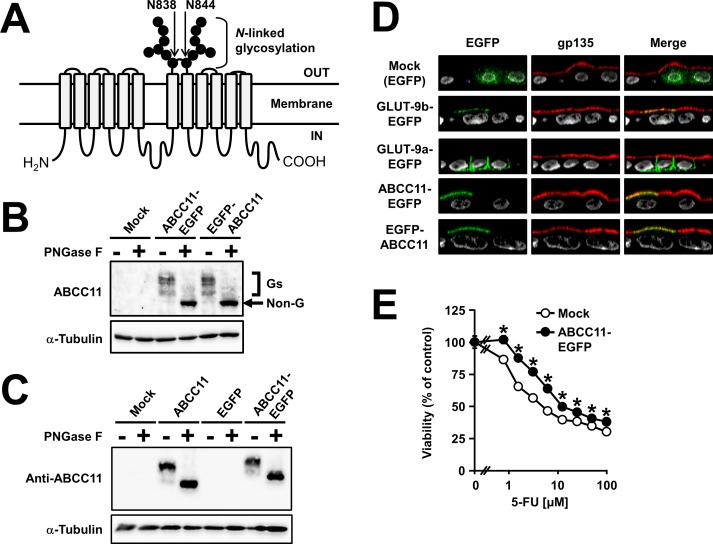
Fig 1. Characterization of ABCC11 fused with EGFP, expressed in MDCKII cells.
(A) Schematic illustration of ABCC11 protein. ABCC11 has two N-linked glycosylation sites, N838 and N844, in an extracellular loop between transmembrane helices 7 and 8. (B) Glycosylation status and expression of ABCC11-EGFP and EGFP-ABCC11 in MDCKII cells. Cell lysates were prepared 72 h after the transfection, and subsequently subjected to immunoblotting after treatment with or without PNGase F. The immunoreactive bands, corresponding to the glycosylated forms (Gs) of EGFP-fused ABCC11 protein, were disappeared after PNGase F treatment. The apparent molecular weight value of the non-glycosylated form (Non-G) of EGFP-fused ABCC11 protein was about 180,000. α-Tubulin: a loading control. (C) Glycosylation status and expression of non-tagged ABCC11 and ABCC11-EGFP in HEK293 cells. Cell lysates were prepared 72 h after the transfection and treated with or without PNGase F, and subsequently subjected to immunoblotting using the anti-ABCC11 antibody. α-Tubulin: a loading control. (D) Apical localization of ABCC11-EGFP and EGFP-ABCC11 in MDCKII cells 72 h after the transfection. An endogenous apical membrane marker gp135 was immunostained using anti-gp135 antibody (red). Nuclei were stained with TO-PRO®-3 iodide (gray). All panels show the Z-sectioning images. Mock (EGFP): a control vector; GLUT-9b-EGFP: a positive control for apical localization; GLUT-9a-EGFP: a negative control for apical localization. (E) 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) resistance activity of MDCKII/mock cells and MDCKII/ABCC11 WT-EGFP cells. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. n = 8. Where vertical bars are not shown, the S.E.M. was contained within the limits of the symbol. Statistical analyses for significant differences were performed according to Student’s t test (*, P < 0.01 compared with mock).