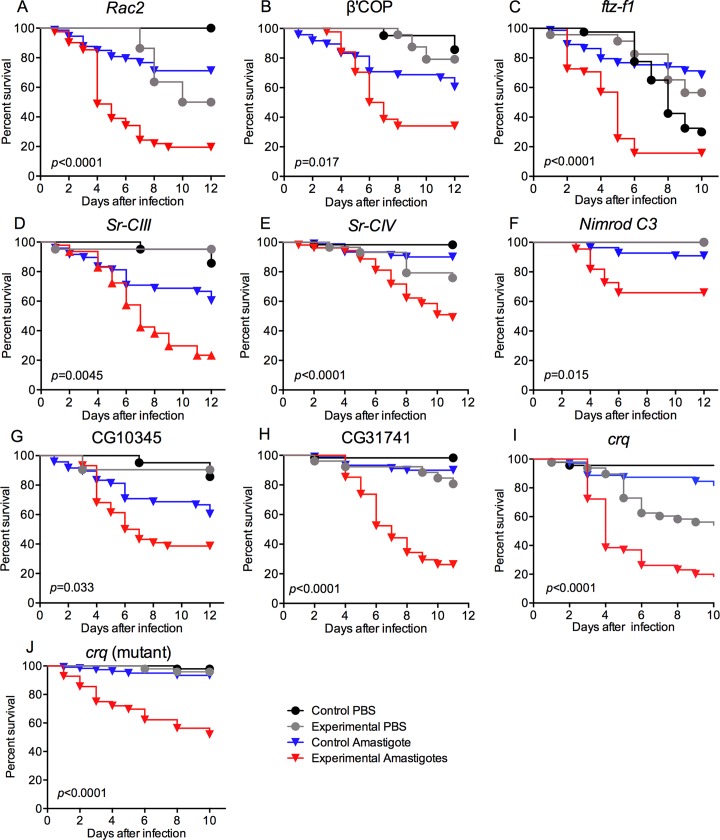
Fig 3. An in vivo RNAi screen identified factors required for Drosophila resistance to L. amazonensis infection.
Nine hemocyte-expressed factors were identified as being required to control Leishmania infection after screening a collection of 32 RNAi or mutant lines (Table 1). Three general phagocytic factors (Rac2, β’COP and ftz-f1, A-C), and six scavenger receptors (D-I) were identified. The receptor hits fell into three classes: two were Class C receptors (a group unique to some Diptera) (D, E), one Nimrod type (F), and three CD36-like receptors (SR-B family): CG10345, CG31741 and croquemort (G-J). Control flies for all RNAi assays included the Hml(Δ)-Gal4 driver but no UAS-RNAi (A-I), while heterozygous flies were used as controls for the crq mutant (J). At least 60 flies were used per sample, survival curve analysis was performed using a Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test, indicated p-values were determined from the comparison of control and RNAi/mutant-infected flies.