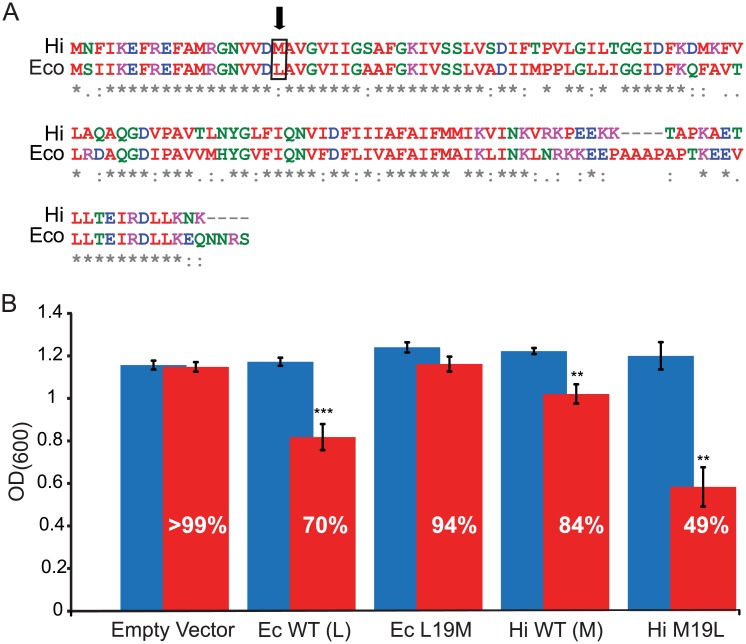
Fig 2. Mutational analysis provides additional evidence that MscL L19 contributes to the binding site of, and increased sensitivity to, DHS.
(A) Sequence alignment of two MscL homologs from E. coli (Ec) and H. influenzae (Hi) showing the difference in sequence at amino acid 19 (boxed and arrow). (B) Average OD600 and SEM from six independent experiments are shown for both WT and mutations of E. coli MscL (Ec) and H. influenzae MscL (Hi) after 240 min in the presence (red bars) or absence (blue bars) of 6.25 μM DHS. The percentage of growth in the presence of DHS, relative to the no DHS, is shown. Note that changing the Ec-MscL L19 to M decreases DHS sensitivity, while changing Hi-MscL M19 to L increases sensitivity. n = 6, **p < .005, ***p <. 0005 versus no DHS added 2-tailed paired t test.