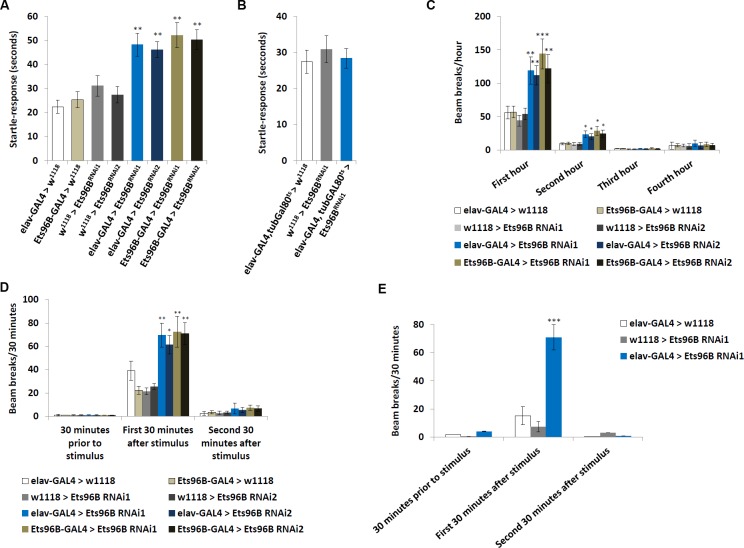
Fig 5. Ets96B knockdown during development induces a heightened startle-response.
(A, B) Startle-response test demonstrating Ets96B knockdown males have a hyperactive startle-response. (A) Ets96B knocked down throughout development using UAS-Ets96BRNAi1 or UAS-Ets96BRNAi2 crossed to the pan-neuronal driver elav-GAL4 (B) Ets96B knocked down only in adults using UAS-Ets96BRNAi1 crossed to the pan-neuronal driver and temperature sensitive allele of the GAL4 inhibitor GAL80 elav-GAL4, tub-Gal80ts. (A, B: n = 50 males per strain; ** P<0.01 compared with controls, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons). (C) The DAMS system was used to monitor locomotion for the first four hours flies were placed in the system. (D) The DAMS system was used to monitor locomotion prior to and after light stimulation. (E) The DAMS system was used to monitor locomotion prior to and after sound stimulation (65–70 dB). Only Ets96BRNAi1 was used for this assay. (C-E: n = 30–60 males per strain; * P < 0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P < 0.005 compared with controls, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons) In all graphs error bars = SEM.