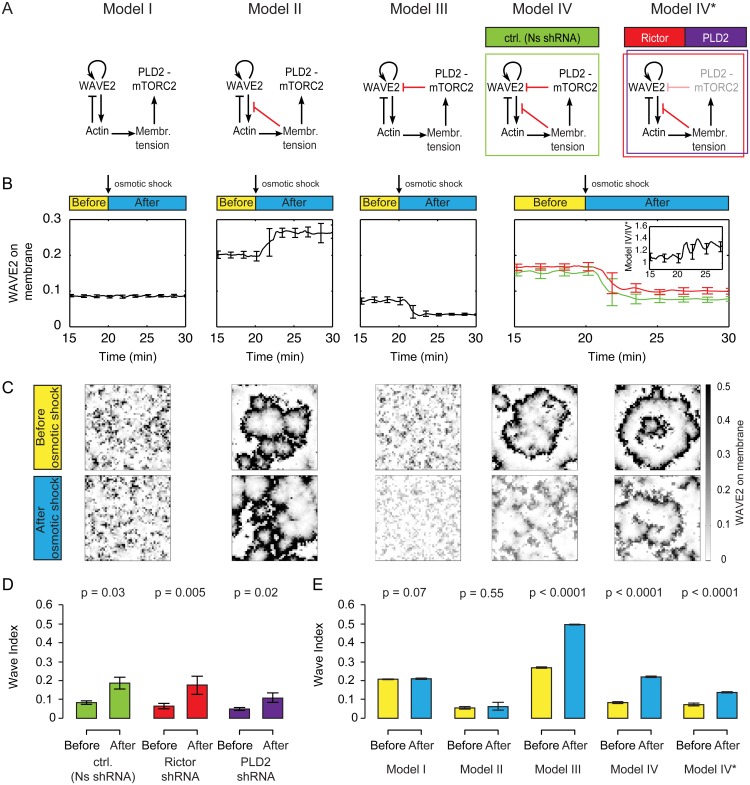
Fig 5. Probing possible topologies of membrane tension-based inhibition of actin network assembly.
(A) Schematic of the different network topologies investigated. Model I: WAVE2 complex dynamics in the absence of tension-mediated inhibition of actin polymerization (see also S5B Fig for early time points). Model II: Global inhibition of actin polymerization by membrane tension only. Model III: Global inhibition of the WAVE2 complex by mTORC2 only. Model IV: Two distinct negative feedbacks from membrane tension to actin network assembly (from tension to actin polymerization and from PLD2–mTORC2 to the WAVE2 complex). Model IV*: Model IV with reduced mTORC2 mediated feedback strength, reflecting our shRNA lines. See Materials and Methods and S1 Text for details of the simulation. (B) WAVE2 complex on the membrane before and after hypo-osmotic shock in the different models. Mean ± SD of 20 stochastic simulations. Only the models with the link from PLD2–mTORC2 to WAVE2 (Model III and Model IV) match our experimental observation of tension-based decreases in WAVE2 association with the membrane (Fig 4C and 4D). Inset: Ratio of models IV, IV*, showing that the difference is larger after osmotic shock. (C) Snapshots of typical simulations before and after osmotic shock (simulated as a step increase in membrane tension of 80 μN/m). See S5 Movie. (D) Quantification of the Wave Index (WI) in control (Ns shRNA), Rictor, and PLD2 shRNA cells before and after osmotic shock. Mean ± SEM. Data used from Fig 4D. (E) Quantification of the Wave Index in the different models before and after osmotic shock. Mean ± SD of 20 stochastic simulations. Model IV exhibits the expected increase of WI upon osmotic shock and shows a similar level of WI to experimental cells (Fig 5D). Ncells/simulations: D = 20 (Ns shRNA), 15 (Rictor shRNA), and 13 (PLD2 shRNA). E = 20 each condition. Statistics: Mann-Whitney test.