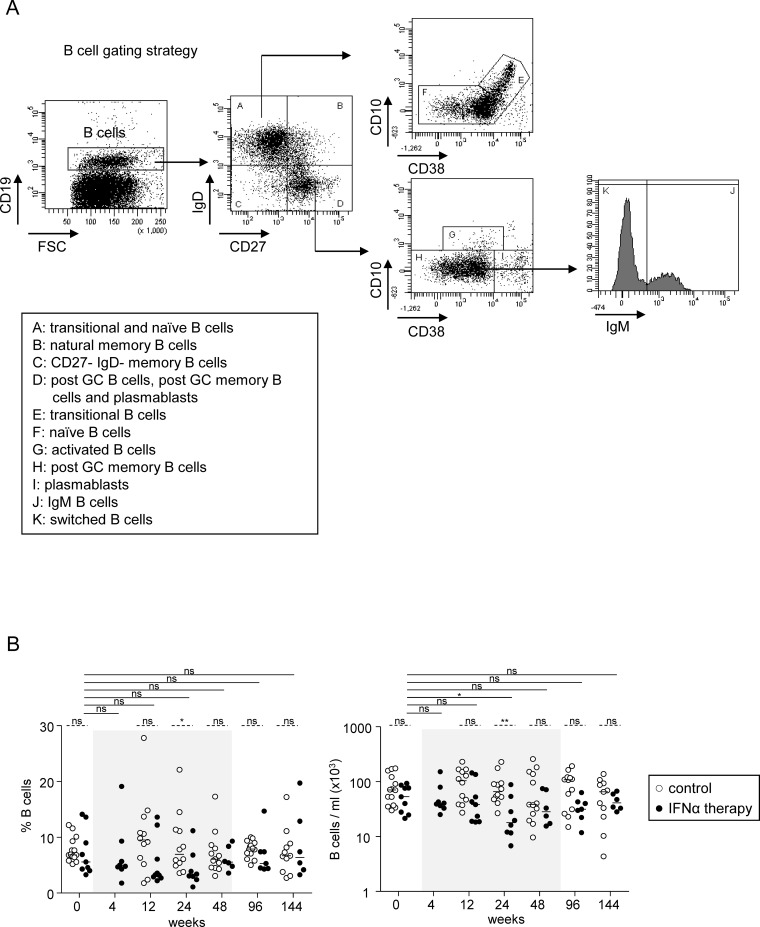
Fig 1. B-cell subsets during Peg-IFN-α therapy.
(A) B-cell gating strategy. The peripheral B-cell subsets were classified according to the most common lineage/differentiation markers CD19, CD10, CD27, CD38, IgD, and IgM. B-cell subsets were defined as: transitional B cells (CD19+CD27-IgD+CD10+CD38high); naive B cells (CD19+CD27-IgD+CD10-CD38low); natural memory B cells (CD19+CD27+IgD+); post-GC memory B cells (CD19+CD27+IgD-CD10-CD38low); plasmablasts (CD19+CD27+IgD-CD10- CD38high); CD27-IgD- memory B cells (CD19+CD27-IgD-) and activated B cells (CD19+CD27+IgD-CD10+CD38low). Post-GC memory B cells were further subdivided into IgM+ and IgM- switched B cells. Representative dotplots from one patient with CHB infection. (B) Modulation of total B cells by Peg-IFN-α. Frequency (within PBMC) and absolute numbers of total B cells in patients with CHB infection treated with nucleos(t)ide analog alone (open circles, n = 11–14) or together with Peg-IFN-α (black circles, n = 8–9). The gray area represents the period of Peg-IFN-α administration. Bars represent median. P values were calculated using the Wilcoxon test (straight lines) or the Mann-Whitney test (dashed lines). * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.