FIGURE 2.
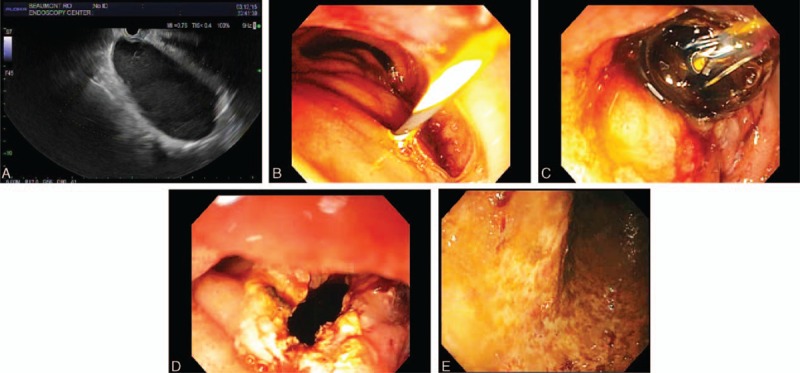
Progressive stages of endosonographic therapy to decompress a highly symptomatic and very long duodenal duplication cyst. A, Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) revealed an oval, intraluminal (subepithelial), anechoic lesion, that endosonographically originated from within the submucosa (layer 3), consistent with duodenal duplication cyst. The cyst arose from muscularis propria of descending duodenum just distal to the papilla, extended deeply into the third portion of duodenum, and contained significant debris within it. B, The duodenal cyst was punctured using a 19 gauge needle; thick, dark fluid was aspirated; a 0.035 in. Jagwire was advanced via the needle into the cyst; the needle was withdrawn; a needle-knife papillotome was fed over the Jagwire; and the cyst wall was incised using the papillotome. C, The papillotome was exchanged with a pyloric balloon dilator, and the aperture was serially dilated up to 18 mm using increasingly larger balloons. D, EGD reveals a wide aperture after progressive balloon dilatation. E, The echoendoscope was withdrawn and a pediatric colonoscope was intubated and advanced into the cyst, and 800 cc of dark, brown fluid was aspirated via the colonoscope This endoscopic photograph shows the mucosa within the cyst has no evident lesions after cyst aspiration.
