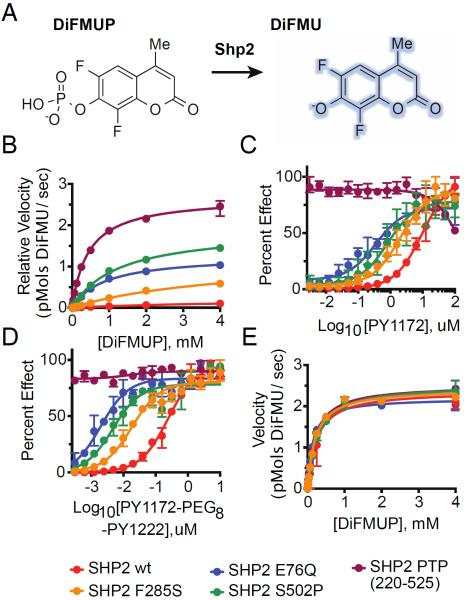
Figure 4. Cancer-Associated SHP2 Mutations Increase Basal Phosphatase Activity and Sensitivity to IRS-1 Phosphopeptide ligand Stimulation.
(A) Schematic illustrating DiFMUP dephosphorylation by SHP2. (B) Basal enzymatic trajectories of wild-type and cancer-associated SHP2 proteins across varying concentrations of DiFMUP. (C) Enzymatic activity of SHP2 proteins (0.05 nM) across varying concentrations of an IRS-1-derived monophosphorylated peptide. (D) Identical experiment to C but with synthetic bisphosphorylated peptide derived from IRS-1. (E) Phosphatase activity of SHP2 proteins (0.01 nM) at saturating concentrations of a double-phosphorylated peptide derived from IRS-1 (6 μM) across varying concentrations of DiFMUP. Velocity data is shown as mean ± standard deviation and was fit to the standard Michaelis-Menten equation to extrapolate kcat and KM values.