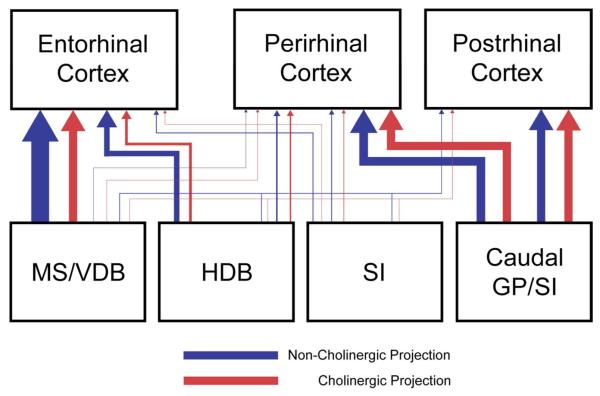
Figure 11.
Summary of the topographic organization of BF projections to the perirhinal, postrhinal, and entorhinal cortex in rats. Red and blue lines indicate cholinergic and non-cholinergic projections. Thickness of lines indicates the relative strength of projections. The perirhinal and postrhinal cortices receive cholinergic and non-cholinergic projections mainly from the caudal basal forebrain (caudal GP and SI), whereas the entorhinal cortex receives projections mainly from the rostral basal forebrain (MS/VDB). Cholinergic neurons projecting to the perirhinal and postrhinal cortex comprise 26-48% of the total projection neurons (cholinergic and non-cholinergic projection neurons) and 13-30% in the entorhinal cases.