Figure 1.
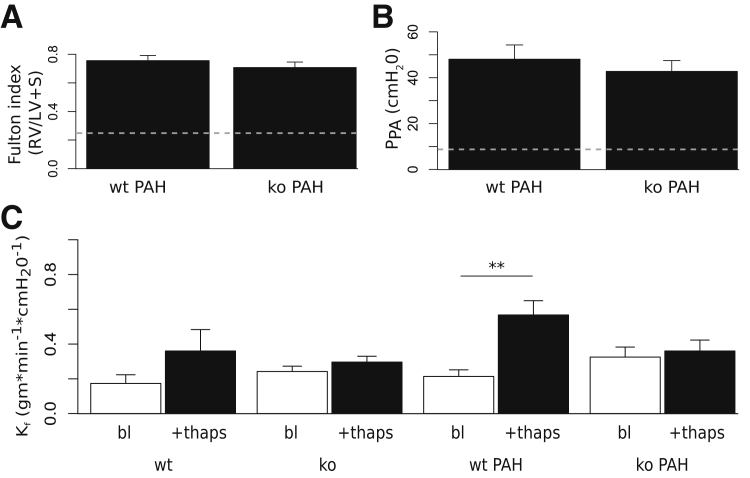
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) attenuates thapsigargin (thaps)–dependent increases in lung vascular permeability in TRPC4-knockout rats. A: After thoracotomy of anesthetized hypertensive wild-type (wt PAH) and TRPC4-knockout (ko PAH) rats, hearts were dissected, cut at the septum, and weighed. Fulton indexes for both groups were calculated as the right ventricular weight (RV), divided by the left ventricular weight including the septum (LV + S). Values were not significantly different between groups. B: Pulmonary arterial pressure was measured (PPA) for both wt PAH and ko PAH groups. There is no significant difference between PPA for either group. C: Lung filtration coefficients (Kf) were measured before (bl) and after stimulation with 75 μmol/L thaps. Thapsigargin induces a significant increase in lung vascular permeability in wild-type hypertensive rats that is abolished in TRPC4-deficient rats. n = 6 to 11 for all groups. ∗∗P < 0.01.