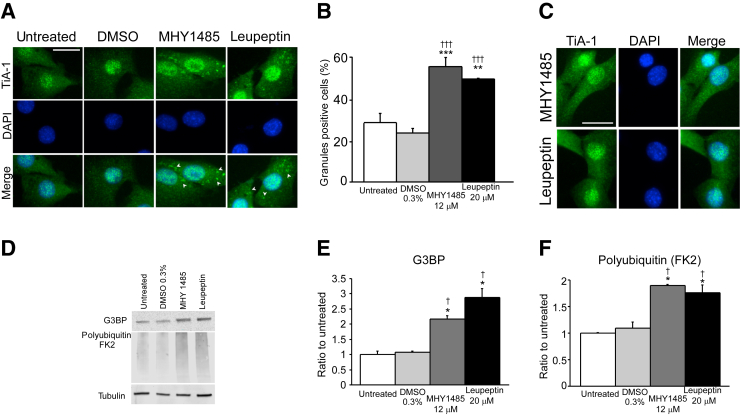
Figure 2.
Autophagy and lysosome inhibitors delay stress granule resolution after arsenite exposure. A: Cells treated with autophagy (12 μmol/L MHY1485) or lysosome (20 μmol/L leupeptin) inhibitors present more stress granules than untreated or 0.3% DMSO-treated cells after left to recover for 1 hour from arsenite exposure. Arrowheads indicate stress granules. B: Quantification of panel A. C: MHY1485 and leupeptin treatment does not show stress granules in the absence of arsenite exposure. D: Similarly, cells analyzed by immunoblot 1 hour after exposure with 200 μmol/L arsenite present augmented levels of the stress granule marker G3BP and polyubiquitylated proteins. E and F: Quantification of panel D. n = 100 cells per well (3 wells per condition) (C). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 versus untreated; †P < 0.05, †††P < 0.001 versus 0.3% DMSO. Scale bars = 50 μm (A and C). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; FK2, mono- and polyubiquitylated proteins antibody; G3BP, RasGAP SH3-binding protein; TiA-1, T-intracellular antigen-1.