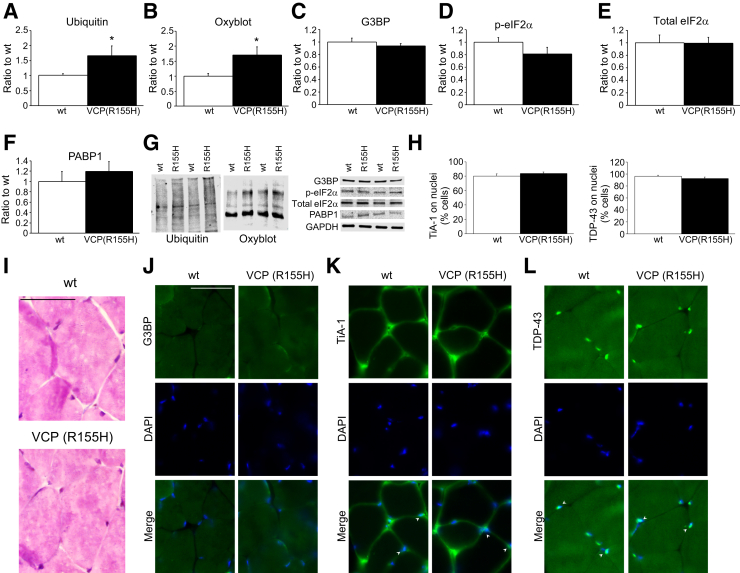
Figure 6.
Oxidative stress but not stress granule markers are increased in the IBMPFD model: the VCPR155H-KI mouse. A: Immunoblot analysis of skeletal muscle lysates shows augmented ubiquitinylated proteins on 15- to 18-month-old VCPR155H-KI mice compared with wt skeletal muscle lysates of the same age. B: Similarly, the oxyblot assay reveals increments on oxidated proteins on skeletal muscle of VCPR155H-KI mice compared with wt mice. C–F: However, G3BP (C), p-eIF2α (D), total eIF2α (E), and PABP1 (F) protein levels are similar between genotypes. G: Representative blots for the different proteins analyzed. H: TiA-1 and TDP-43 present major nuclear localization when analyzed by immunofluorescence. I: Hematoxylin and eosin staining shows no major histologic differences between the wt and VCPR155H-KI skeletal muscle. J–L: Similarly, no differences are detected when skeletal muscle was stained for G3BP (J), TiA-1 (K), and TDP-43 (L). Arrowheads indicate nuclear localization of TiA-1 and TDP-43 proteins. n = 8 wt and 7 VCPR155H-KI (R155H) mice (G). ∗P < 0.05. Scale bars = 50 μm. eIF2α, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; G3BP, RasGAP SH3-binding protein; IBMPFD, inclusion body myopathy associated with Paget disease of bone and frontotemporal dementia; KI, knockin; p, phosphorylated; PABP1, poly(A)-binding protein 1; TDP-43, transactive response DNA-binding protein 43; TiA-1, T-intracellular antigen-1; VCP, valosin-containing protein; wt, wild-type.