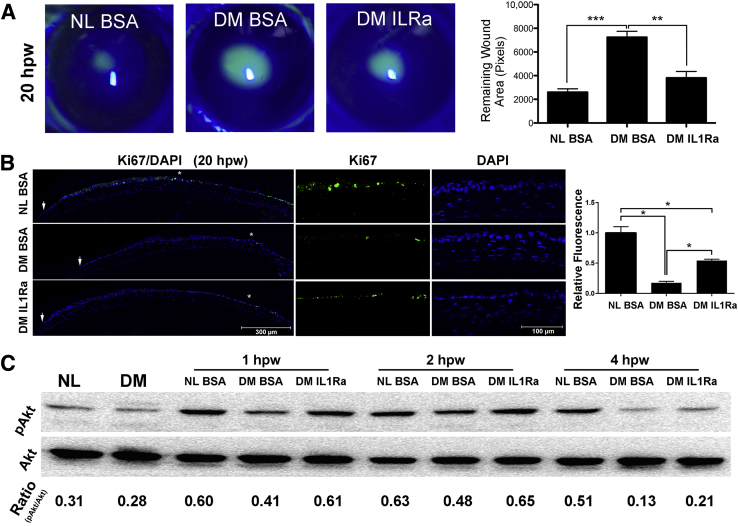
Figure 3.
Effects of exogenous IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) on diabetic epithelial wound healing rate, proliferation, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt activation. A: Normal (NL) mice were injected subconjunctivally with 5 μL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA), diabetes mellitus (DM) mice were subconjunctivally injected with 5 μL PBS containing 0.1% BSA, left eyes, or IL-1Ra (25 ng/μL, diluted from anakinra injection solution), right eyes, 4 hours before epithelium debridement. Corneas were imaged at 20 hours after wounding (hpw), and the wound sizes were calculated and results were presented as the mean of the remaining wound area. B: Proliferation assay via immunofluorescence staining for Ki-67. Staining was quantitated by calculating the area covered with green in each image (showing cornea from limbal region to epithelial leading edge) using ImageJ version 1.48v. The result was presented as relative fluorescence with the value derived from NL healing corneal sections as 1. Arrows indicate the leading edge of healing epithelium. Areas marked with asterisks are shown at higher magnification to the right. Two independent experiments were performed. C: Western blot analysis of phospho-Akt (pAkt) with Akt as the internal control. The intensity of each band was digitized by ImageJ, and ratio of pAkt/Akt was calculated and presented. Data are given as means ± SEM (A and B). n = 5 (A); n = 3 (B). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance).