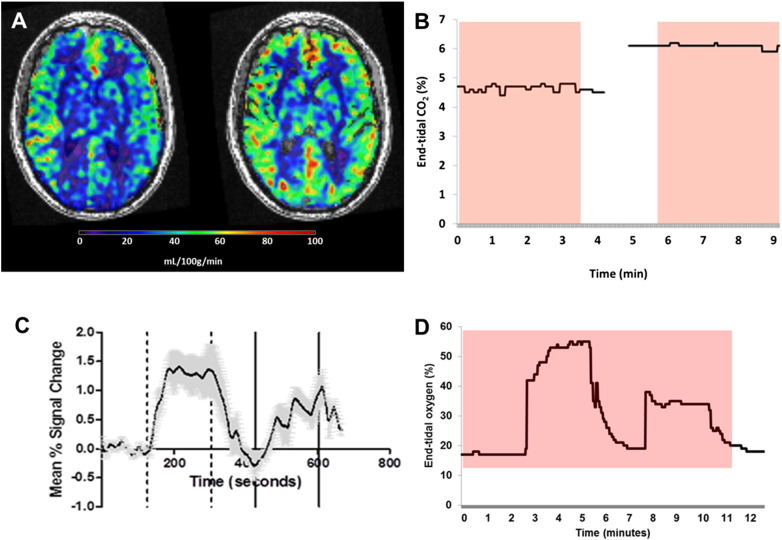
Fig. 2.
Steady-state and dynamic respiratory challenges. (A) Arterial spin labelling (ASL) MRI performed whilst receiving air (left) and 6% CO2/air mixture (right) in a patient with cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL), demonstrating increased CBF in response to hypercapnia. Delivery of a 6% CO2 gas mixture caused a change in end-tidal CO2 (B) and separate scans were performed during each steady state. The red box represents the duration of the ASL scans. Continuous imaging can allow the application of repeated challenges and assess temporal resolution of signal in relation to gas concentrations. In (C) T2* signal changes vary over an 11min fMRI in 4 normal volunteers given a dual hyperoxic challenge. Changes in end-tidal oxygen concentration for one patient receiving this challenge is shown in (D) and can be correlated with signal changes. The red box represents the duration of the scan.