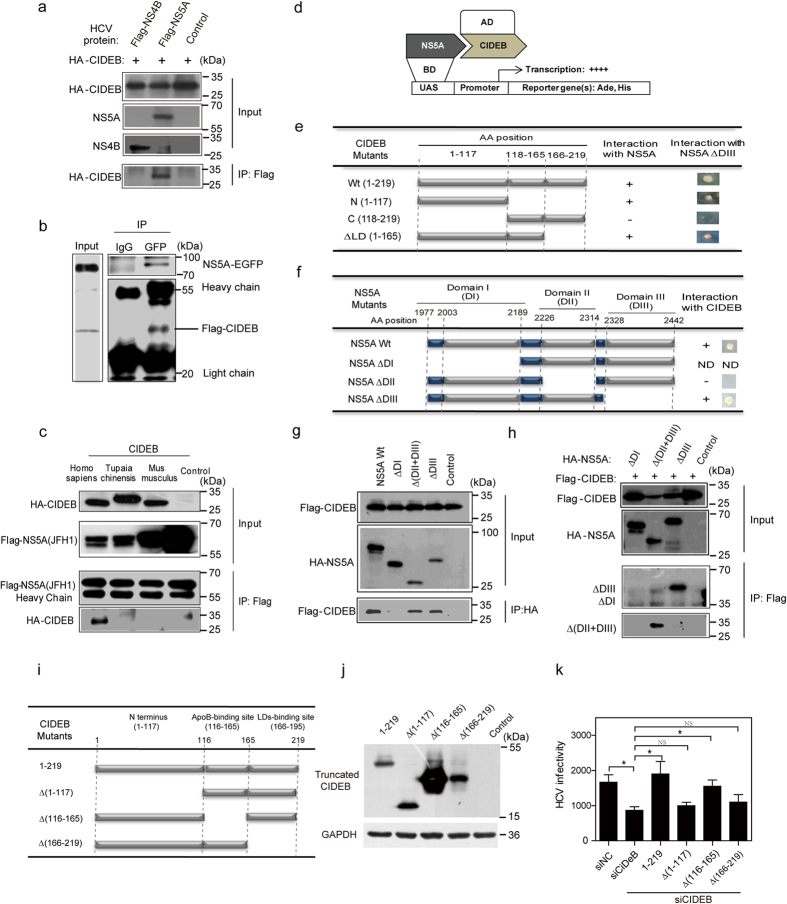
Figure 4. CIDEB interacts with the HCV NS5A protein, and the N terminus of CIDEB and domain I of NS5A are essential for the CIDEB-NS5A interaction.
(a) Co-IP assay to determine the interaction of exogenous HA-CIDEB with Flag-NS5A and Flag-NS4B in HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were subjected to IP with an anti-Flag antibody and then immunoblotted with an anti-HA antibody. (b) Co-IP assay to determine the interaction of exogenous Flag-CIDEB with endogenous NS5A-EGFP in HCV-Jc1EGFP-infected Huh7.5.1 cells transfected with pReceiver-Flag-CIDEB. (c) Co-IP assay to determine the interaction of exogenous CIDEB from different species (Homo sapiens, Tupaia chinensis, and Mus musculus) with Flag-NS5A (from HCV-JFH1) in HEK293T cells. (d) The principle of the yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assay: AH109 transfected with HCV NS5A mutants mated with Y187 transfected with CIDEB mutants; interaction between two proteins is indicated by the activation of the reporter genes HIS3 and ADE, which allows the mated yeast cells to grow on plates containing SD/–Ade/–His/–Leu/–Trp (+ + + +). UAS: upstream activating sequence; AD: activation domain; BD: DNA-binding domain. (e) Schematic of the tested CIDEB constructs and screening results for the CIDEB-NS5A interaction. (f) Schematic of the tested NS5A constructs and screening results for the CIDEB-NS5A interaction. ND: cannot be determined due to autoactivation. (g,h) Co-IP assays to identify the specific domain of NS5A responsible for the CIDEB-NS5A interaction. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with the expression vectors for Flag-CIDEB and truncated HA-NS5A. (g) The cell lysates were subjected to IP with an anti-HA antibody and then immunoblotted with an anti-Flag antibody. (h) The cell lysates were subjected to IP with an anti-Flag antibody and then immunoblotted with an anti-HA antibody. (i–k) The effect of siRNA-resistant truncated CIDEB on HCV production in siCIDEB-pretreated Huh7.5.1 cells. (i) Schematic of CIDEB and its truncations. (j) Western blot analysis to detect the overexpression of siRNA-resistant CIDEB and its truncations. (k) The effect of siRNA-resistant truncated CIDEB overexpression on the extracellular HCV titer in siCIDEB-pretreated Huh7.5.1 cells. The results are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments; *P < 0.05).