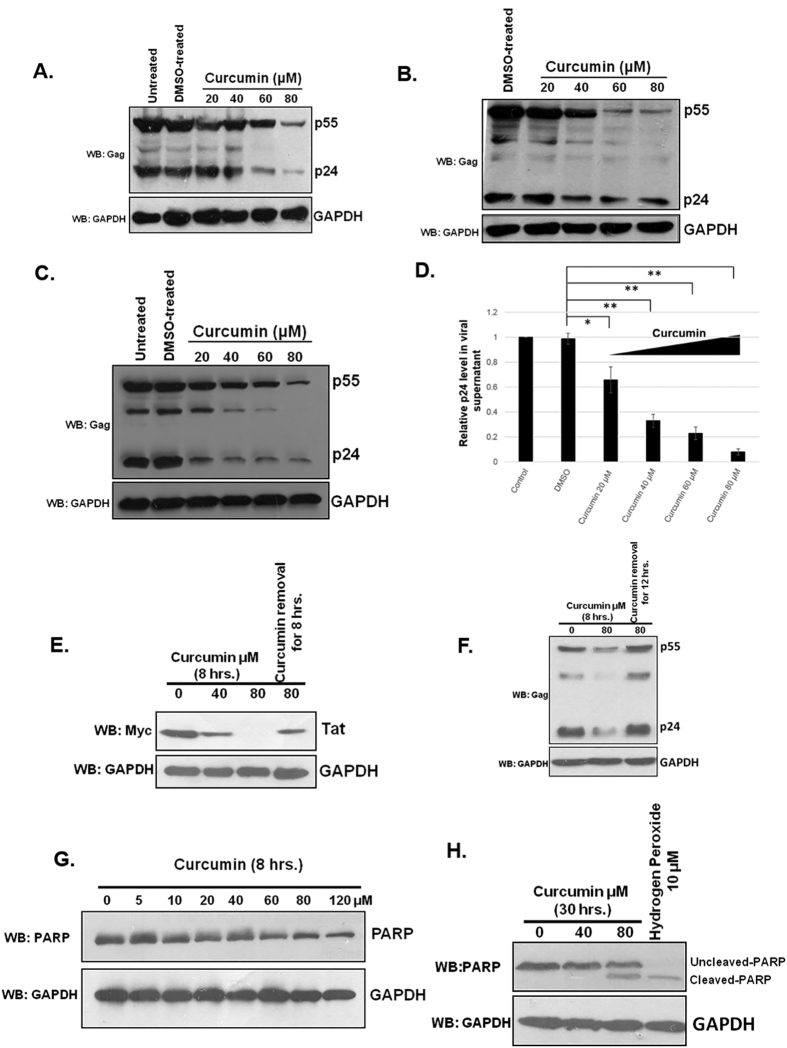
Figure 3. Curcumin treatment resulted in a reduced production of HIV-1 virions.
(A) HEK-293T cells were transfected with 1 μg pNL4-3, after 36 hrs the medium was changed and curcumin was added from 20–80 μM for 12 hrs. The cells were lysed and probed for p24 Gag protein. Medium containing viral supernatant was used to infect TZM-bl cells. (B) TZM-bl cells were infected with viral supernatant obtained from previous experiment and the cells were further incubated for 24 hrs followed by lysis and measurement of p24 level. (C) J1.1 cells were stimulated with 20 ng/ml of TNF-α for 12 hrs subsequently the medium was replaced with fresh complete RPMI containing curcumin and TNF-α as indicated. The cells were lysed and blotted for p24 level whereas the cell culture medium containing virions were used to detect viral load by direct ELISA. (D) The virus containing medium from previous experiment was coated on 96 well ELISA plate and probed with p24 antibody, the average value of p24 from three independent ELISA experiments was plotted with respect to curcumin concentration. P value was calculated by a two-tailed t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; NS, not significant). (E) Myc-Tat transfected HEK-293T cells were treated with curcumin for 8 hrs subsequently it was removed and fresh complete DMEM was added and incubated for 8 hrs followed by immunoblotting for Tat. (F) Curcumin treatment was carried out to pNL4-3 transfected HEK-293T cells followed by replacement with fresh DMEM medium and further incubation for 12 hrs. The p24 protein level was measured by western blotting. (G) HEK-293T cells were treated with indicated doses of curcumin for 8 hrs followed by western blotting for PARP. (H) Curcumin treatment was carried out for 30 hrs followed by western blotting to detect un-cleaved and cleaved PARP. As a control the cells were treated with hydrogen peroxide and blotted for PARP.