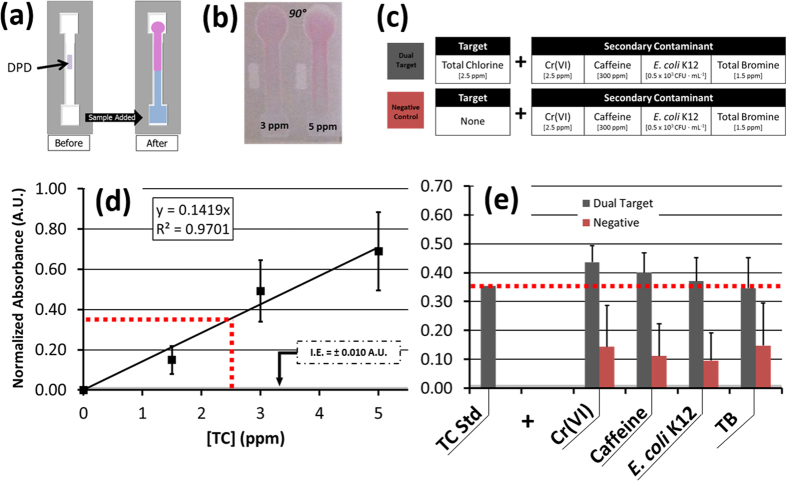
Figure 5.
(a) A colorimetric μPAD assay for detecting total chlorine (TC) using N,N-diethyl-p-phenyldiamine sulfate (DPD). (b) With increasing TC concentration, an increasing lavender color change is produced, as measureable by a change in normalized absorbance of the green band (λmax = 520 nm) reflected light intensity. (c) Dual-target and negative control solutions were assayed and compared with a (d) DPD-TC standard curve created by single-target μPAD detection of TC concentrations using DPC (n = 4). (e) There was no significant difference in normalized absorbance measured between the dual target control solutions and 2.5 ppm TC. Compared with the negative control solutions, there was only a significant difference between 2.5 ppm TC and E. coli K12 (p < 0.05).