Fig. 1.
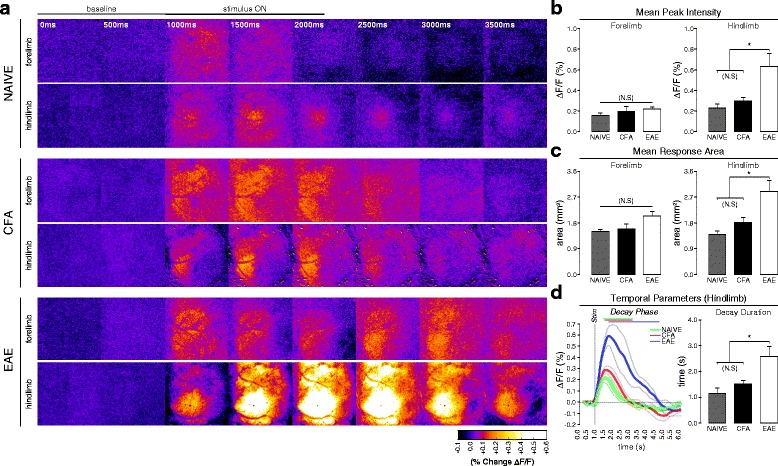
In vivo FA imaging of vibrotactile-evoked responses in S1 at the pre-symptomatic stage of EAE. a Balanced-contrast pseudocolored (%∆F/F) montages of representative hindlimb and forelimb responses in S1 of naïve, CFA, and pre-symptomatic EAE (7–9 dpi) animals. b Group mean (±S.E.) signal intensities at peak FA response, calculated from the “cortical map” area as a percent change in fluorescence vs. baseline (%∆F/F). Pre-symptomatic EAE animals (n = 4) exhibited significantly intensified responses to vibrotactile stimulation of the hindlimb, but not the forelimb, compared to naïve (n = 3) and CFA controls (n = 5). Naïve and CFA responses did not significantly differ from each other (one-way ANOVA, p = 0.012; all pairwise post hoc comparisons by Holm-Sidak method). c Group mean (±S.E.) areas of the FAI response, calculated from (gray-value averaged) z-projections of the response phase, and defined as the region exhibiting a ≥50 %-of-maximal increase in fluorescence vs. baseline (%∆F/F). Pre-symptomatic EAE animals (n = 4) exhibited significantly expanded hindlimb, but not forelimb, responses compared to naïve (n = 3) and CFA-controls (n = 5). Naïve and CFA responses did not significantly differ from each other (one-way ANOVA, p = 0.009; all pairwise post hoc comparisons by Holm-Sidak method). d Grand-average FA signal traces (thick traces; ±S.E. thin traces) of hindlimb responses in naïve (green trace, n = 3), CFA (red trace, n = 5), and pre-symptomatic EAE (blue trace, n = 4) animals. Gray vertical bar shows time of stimulus onset. Overlying bars indicate signal decay phase (time from peak signal intensity to x-axis intercept). At the right, group mean (±S.E.) decay phase durations as bar plot. Pre-symptomatic EAE animals exhibited significantly prolonged FAI decay phase durations vs. naïve and CFA animals. Naïve and CFA responses did not differ significantly from each other (one-way ANOVA, p = 0.013; all pairwise post hoc comparisons by Holm-Sidak method)
