Fig. 6.
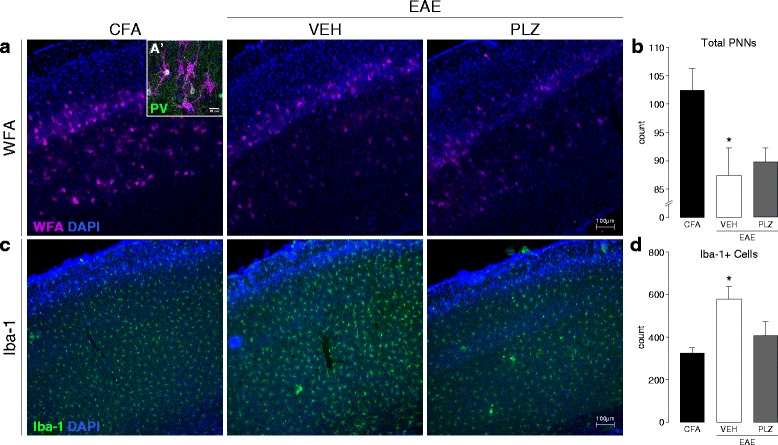
Microglial activation and peri-neuronal net integrity in S1, and the effects of PLZ, in established EAE. a Representative fluorescence photomicrographs of WFA+ staining (PNNs) in S1 from control (CFA) animals and EAE animals treated from 7 dpi with either (VEH) or (PLZ). A’ (inset) High-magnification confocal photomicrograph depicting PNNs (WFA+, magenta) surrounding PV+ interneurons (green) in S1HL. DAPI (cell-nuclei) counter-stain is shown in blue. b Group mean (±S.E.) total PNN counts from WFA+ stained S1HL of CFA (n = 6), VEH-treated EAE (n = 7), and PLZ-treated (n = 4) EAE animals (21 dpi). VEH-treated EAE animals exhibited significantly reduced PNN-counts in S1HL vs. CFA controls. PNN counts from the PLZ-treated EAE mice were also significantly reduced compared to CFA. PNN counts were approximately equivalent (not significant, p > 0.05) between both the VEH-treated and PLZ-treated EAE groups (one-way ANOVA, p = 0.021, post hoc comparisons vs. CFA controls by Dunnett’s method). c Representative fluorescence photomicrographs of Iba-1+ staining (activated microglia/macrophages) in S1HL of CFA animals and EAE animals treated chronically from 7 dpi with either (VEH) or (PLZ). d Group mean (±S.E.) counts of Iba-1+ cells in S1HL of CFA (n = 6), VEH-treated EAE (n = 7), or PLZ-treated EAE (n = 4) animals. VEH-treated EAE animals exhibited significantly increased numbers of Iba-1+ cells in S1HL vs. CFA controls. Chronic treatment of EAE mice with PLZ from 7 dpi reduced the number of Iba-1+ cells in S1HL—EAE-PLZ animals did not differ significantly from CFA controls (one-way ANOVA, p = 0.009, post hoc comparisons vs. CFA controls by Dunnett’s method)
