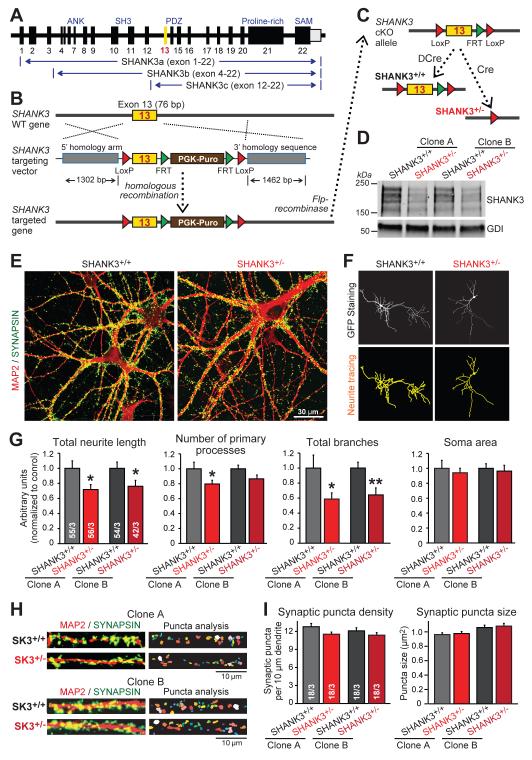
Figure 1. SHANK3 haploinsufficiency impairs dendritic development of human neurons.
A) Diagram of the SHANK3 gene and of the three major SHANK3 transcripts that are blocked by conditional deletion of exon 13 (yellow).
B & C) SHANK3 targeting strategy in human ES cells. Homologous recombination was mediated using recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) (B) and confirmed by PCR (Fig. S1B). The PGK-puromycin resistance cassette (brown box) was excised by Flp-recombinase to generate the conditional KO (cKO) allele (SHANK3+/cKO; panel C). SHANK3+/cKO ES cells were converted into human SHANK3+/+ or SHANK3+/− neurons by co-expression of Ngn2 with either mutant inactive Cre-recombinase (ΔCre) or active Cre-recombinase (Cre).
D) Reduction of SHANK3 protein levels in human SHANK3+/− neurons derived from two independent SHANK3+/cKO ES cell clones.
E) Representative images of SHANK3+/+ and SHANK3+/− neurons (day 21) labeled by double immunofluorescence for MAP2 (red) and synapsin (green).
F) Representative dendritic arborization analyses by MetaMorph software of SHANK3+/+ and SHANK3+/− neurons (sparsely transfected with EGFP).
G) SHANK3 haploinsufficiency impairs dendritic arborization (summary graphs of indicated parameters measured in matching SHANK3+/+ and SHANK3+/− neurons derived from independent SHANK3+/cKO ES cell clones; normalized to SHANK3+/+ controls).
H) Representative images of SHANK3+/+ and SHANK3+/− dendrites stained for MAP2 (red) and synapsin (green) for analysis of synaptic puncta by MetaMorph software.
I) Summary graphs of dendritic synaptic puncta density and size in SHANK3+/+ and SHANK3+/− neurons derived from two independent SHANK3+/cKO ES cell clones.
Data in G and I are means ± SEM. Numbers of cells/independent cultures analyzed are shown in the bars. Statistical significance was evaluated by Student’s t-test, (*, p<0.05; **, p<0.01). For additional data, see Figs. S1, S2.