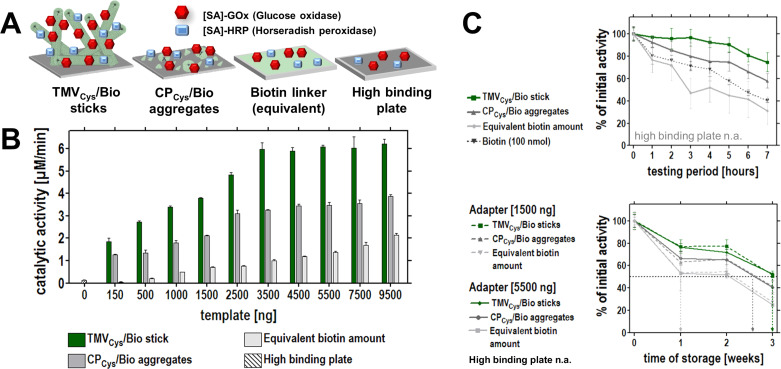
Figure 6.
Influence of TMV adapter scaffolds on enzyme-based glucose detection layouts. A: Schematic drawing of different detection layouts using TMV-derived or linker adapters for the immobilization of enzymes on solid supports, or adsorptively immobilized enzymes on untreated surfaces (layouts with adapters: with TMVCys/Bio rods, CPCys/Bio aggregates, or biotin linkers; without adapters: plain surface). B: Catalytic activities achieved with these layouts using different adapter concentrations, applying the same [SA]-GOx/[SA]-HRP input for colorimetric glucose detection via formation of ABTS* radicals (absorption maximum at λ = 405 nm). TMV adapter templates support the immobilization of substantially increased enzyme activities. C: TMV adapters exert enzyme-stabilizing effects, increasing both the reusability of the immobilized enzyme upon hourly repeated uses (top), and the storage stability over a testing period of three weeks. Initial turnover rates were set to 100 % and the percentage of remaining activities calculated. Degree of reusability: TMVCys/Bio nanorods > CPCys/Bio aggregates > biotin linker > substrate lacking any adapter molecule. For details, see text and reference [132] for details. B/C: Reproduced according to the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License from [132].