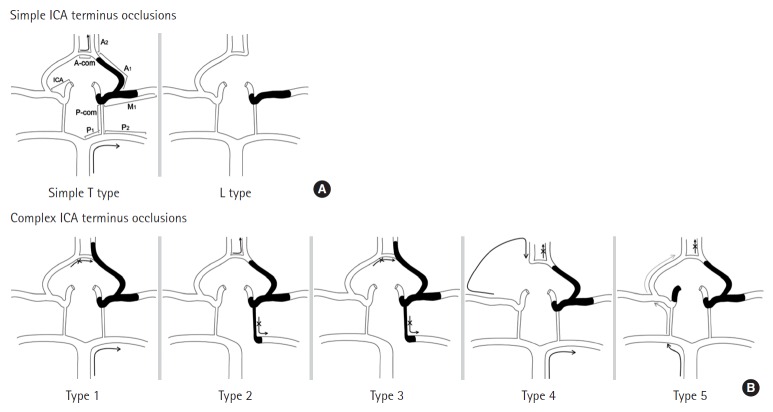
Figure 1.
Simple and complex internal carotid artery (ICA) terminus occlusions. (A) Simple ICA terminus occlusion: the thrombus is confined to the bifurcation of the ICA, ipsilateral M1±A1. The ipsilateral A2 is irrigated by the collateral flow via the anterior communicating artery (A-com). (B) Complex ICA terminus occlusions. Type 1: the thrombus extends beyond the ipsilateral A1 to involve the A2, or agenesis of the anterior communicating artery halts the anterior cerebral artery leptomeningeal collaterals. Type 2: the ipsilateral posterior cerebral artery is also occluded by the distal ICA occlusion. Type 3: combination of types 1 and 2. Type 4: absence of the contralateral A1. Type 5: occlusion of the contralateral ICA. P-com, posterior communicating artery.