Figure 1.
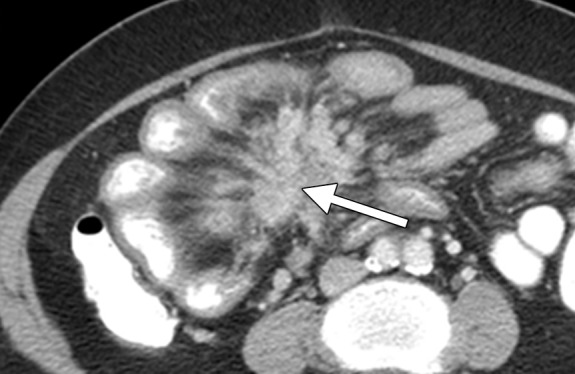
Carcinoid tumor metastatic to the mesentery in a 36-year-old woman with abdominal pain. Axial contrast material–enhanced computed tomographic (CT) image shows radiating nodular soft-tissue strands in the mesentery (arrow), as well as tethering, angulation, and retraction of the small bowel loops producing the characteristic spoke-wheel appearance due to tumor-induced fibrosis and desmoplastic reaction. Most carcinoids originate in the small intestines and secondarily involve the mesentery via direct tumor extension and/or lymphatic spread. Primary intestinal tumor is often difficult to detect at imaging because of its small size.
