Abstract
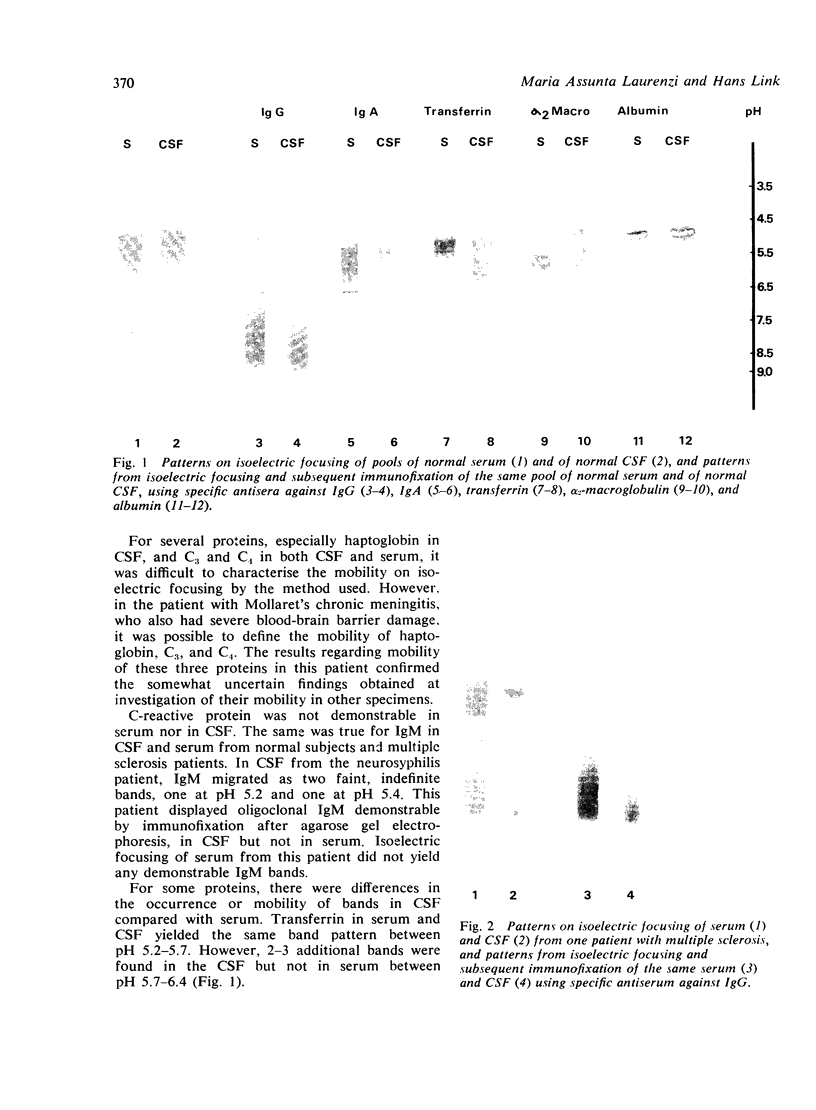
The mobility of 17 different proteins in CSF and serum on isoelectric focusing was investigated by subsequent immunofixation using monospecific antisera. Individual proteins yielded identical, often complex band patterns in normal CSF and serum, except transferrin which gave one to two additional bands between pH 5.8-6.4, and the low molecular wieght beta-trace protein and gamma-trace protein, which gave three bands at pH 7.4, 8.0, and 8.4, and a single band at pH 9.5, respectively, on investigation of CSF but not serum. Polyclonal IgC migrated as multiple bands between pH 4.7-8.6. Oligoclonal IgG in CSF in multiple sclerosis and neurosyphilis migrated between pH 8.6-9.5 and was easily discriminated from other proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud P., Wilson G. B., Koistinen J., Fudenberg H. H. Immunofixation after electrofocusing: improved method for specific detection of serum proteins with determination of isoelectric points. I. Immunofixation print technique for detection of alpha-1-protease inhibitor. J Immunol Methods. 1977;16(3):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmotte P. Gel isoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid proteins: a potential diagnostic tool. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1971 Jul;9(4):334–336. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1971.9.4.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmotte P., Gonsette R. Biochemical findings in multiple sclerosis IV. Isoelectric focusing of the CSF gamma globulins in multiple sclerosis (262 cases) and other neurological diseases (272 cases). J Neurol. 1977 Apr 28;215(1):27–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00312547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryden A., Link H., Norrby E. Cerebrospinal fluid and serum immunoglobulins and antibody titers in mumps meningitis and aseptic meningitis of other etiology. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):852–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.852-861.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellin K. G., Siden A. Aberrant CSF protein fractions found by electrofocusing in multiple sclerosis. A study of 26 cases with clinically verified or probable multiple sclerosis and 2 cases with optic neuritis. Eur Neurol. 1977;15(1):40–50. doi: 10.1159/000114787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellin K. G., Stibler H. CSF-protein patterns in extrapyramidal diseases. Preliminary report with special reference to the protein patterns in Huntington's chorea. Eur Neurol. 1974;12(3):186–194. doi: 10.1159/000114617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellin K. G., Stibler H. Cerebrospinal fluid protein patterns in spasmodic torticollis. Eur Neurol. 1975;13(5):461–475. doi: 10.1159/000114702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellin K. G., Vesterberg O. Isoelectric focusing of CSF proteins in neurological diseases. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Oct;23(2):199–213. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latner A. L. Some clinical biochemical aspects of isoelectric focusing. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Jun 15;209:281–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Tibbling G. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. II. Relation of the concentration of the proteins in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):391–396. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibler H., Kjellin K. G. Isoelectric focusing and electrophoresis of the CSF proteins in tremor of different origins. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Dec;30(2-3):269–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibler H. The normal cerebrospinal fluid proteins identified by means of thin-layer isoelectric focusing and crossed immunoelectrofocusing. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Apr;36(2):273–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbling G., Link H., Ohman S. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):385–390. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]