Figure 1.
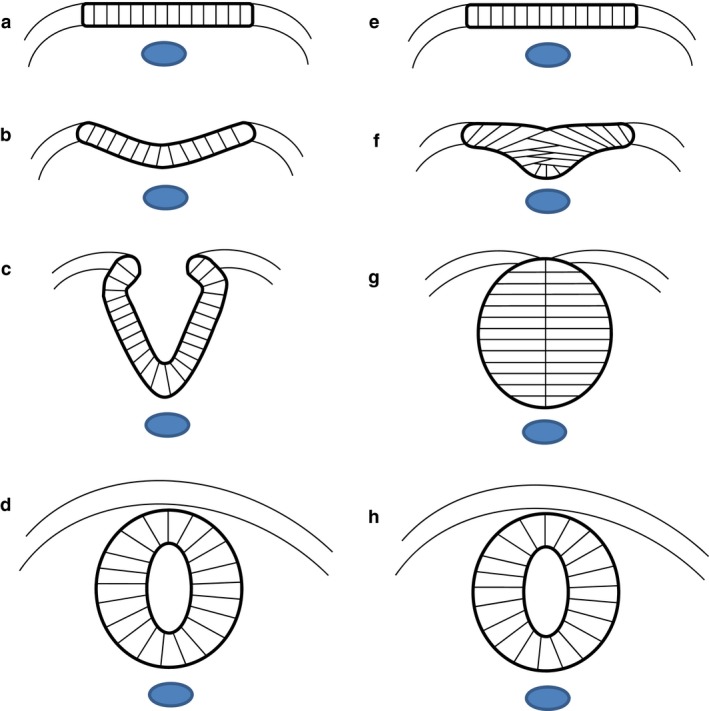
Two strategies of neurulation. (a–d) In most vertebrates, the flat neural plate (a) bends causing the neural folds to elevate and approach each other in the dorsal midline (b, c), where they fuse to form the closed neural tube (d). (e–h) In teleosts, such as the zebrafish, the cells of the neural plate coalesce to form the neural keel (e, f). This structure re‐organizes into the neural rod (g) before cavitating to form the neural tube (h). Images are schematic transverse sections. Blue: notochord.
