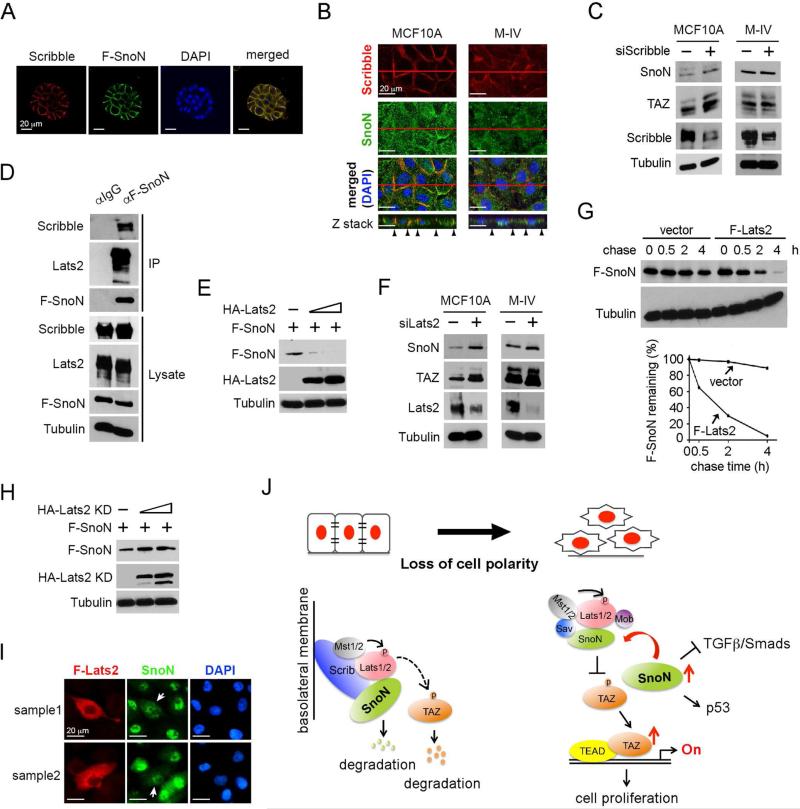
Figure 7. SnoN is regulated by Scribble in a Lats2-dependent manner.
(A) SnoN localized at the basolateral membrane in 3D culture. MCF10A/F-SnoN cells were cultured in 3D IrECM for 6 days, fixed and stained with anti-Scrib (red) or anti-Flag (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Bar, 20 μm. (B) Confocal images showed that SnoN (green) co-localized with Scribble (red) at the basolateral junction in MCF10A cells in 2D, but not in M-IV cells where both proteins have lost the membrane localization. The top panels showed the XY images and the bottom panels were the Z stacks. Black arrowheads indicated the lateral membrane domains. Bar, 20 μm. (C) Reducing Scribble expression led to upregulation of SnoN and TAZ expression in MCF10A cells, but not in M-IV cells. (D) MCF10A cells stably expressing F-SnoN were cultured until reached high cell density and treated with 20 μM MG132 for 6 h. F-SnoN and the associated Scribble and Lats2 were analyzed by co-IP assay. (E) Protein levels were determined by Western blotting in cells transfected with fixed amount of F-SnoN and increasing amounts of HA-Lats2. (F) Reducing Lats2 expression led to increased SnoN and TAZ expression in both MCF10A and M-IV cells. (G) Pulse-chase assay. 35S-labeled F-SnoN was immunoprecipitated from 293T cells transfected with F-SnoN together with or without F-Lats2 and detected by auto-radiography. Quantification of the autoradiograph was shown at the bottom. (H) Cells were transfected with F-SnoN and increasing amounts of HA-Lats2 (KD) and subjected to Western blotting analysis. (I) Immunofluorescence staining of SnoN (green) and F-Lats2 (red) in MCF10A cells showed that overexpression of F-Lats2 (white arrow) resulted in nuclear reduction of SnoN. Images from two cell fields were shown (sample 1 and 2). Bar, 20 μm. (J) A model of mutual regulatory interaction between SnoN and Hippo pathway.