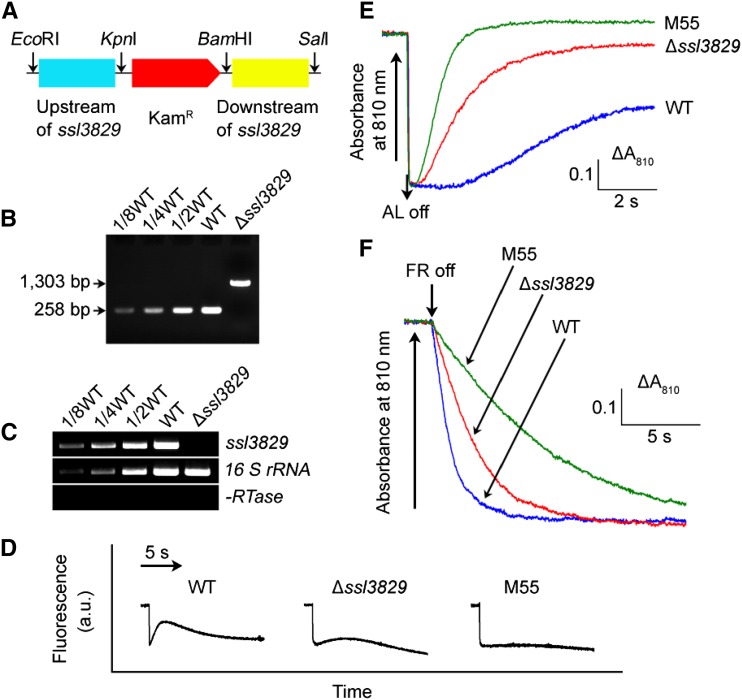
Figure 2.
Deletion of ssl3829 and its effect on NDH-CET. A, Construction of the plasmid used to generate the ssl3829 deletion mutant (∆ssl3829). B, PCR segregation analysis of the ∆ssl3829 mutant using the ssl3829-G and ssl3829-H primer sequences (Supplemental Table S1). C, Transcript levels of ssl3829 in the wild-type (WT) and ∆ssl3829 strains. The transcript level of 16 S rRNA in each sample is shown as a control. The absence of contamination of DNA was confirmed by PCR without reverse transcriptase. D, Analysis of NDH-CET activity by Chl fluorescence. The experimental procedure was as in Figure 1B. M55 is an ndhB deletion mutant (ΔndhB); a.u., arbitrary units. E, Redox kinetics of P700 after termination of AL illumination (800 µmol photons m−2 s−1 for 30 s) under a background of FR light. The cells were illuminated by AL supplemented with FR light to store electrons in the cytoplasmic pool. After termination of AL illumination, P700+ was reduced transiently by electrons from the plastoquinone pool; thereafter, P700 was reoxidized by background FR light. The redox kinetics of P700 was recorded. The P700+ levels were standardized by their maximum levels attained by exposure to FR light. The reoxidation level of P700 was evaluated by the height and the relative rate of redox kinetics of P700. F, Kinetics of the P700+ rereduction in darkness after turning off FR light with a maximum at 720 nm in the presence of 10 µm 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea in wild-type, ∆ssl3829, and M55 strains. The Chl a concentration was adjusted to 20 µg mL−1 before measurement, and curves are normalized to the maximal signal. The rereduction level of P700+ was assessed by the initial reduction rate of P700+.