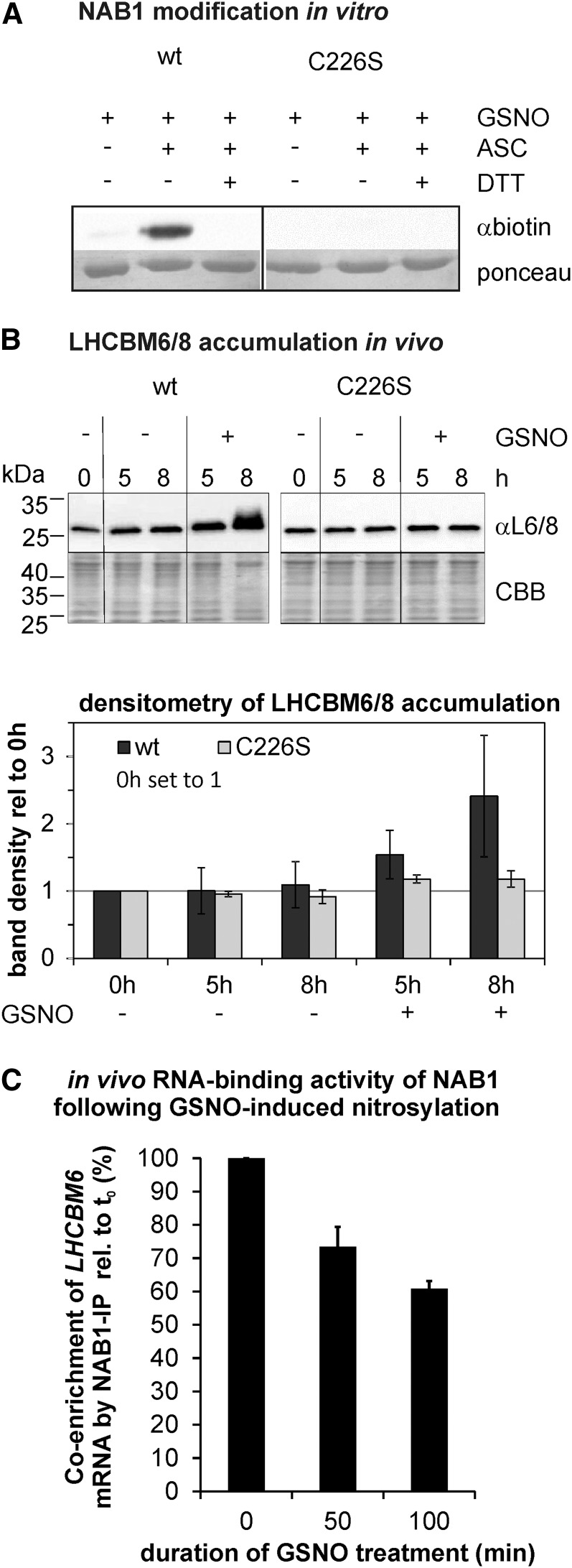
Figure 3.
Nitrosylation of NAB1 at Cys-226 decreases its translation repressor activity. A, In vitro nitrosylation of recombinant NAB1 with GSNO (2 mm). The wild-type version of NAB1 was used along with NAB1C226S. The biotin switch technique was applied to detect S-nitrosylation via immunodetection of the biotin label (αbiotin). Omission of GSNO (−) and addition of DTT (+DTT) served as a control to assess stringency of the assay. Ponceau staining served as loading control. B, Effects of Cys-226 nitrosylation on the accumulation of major light-harvesting proteins LHCBM6/8. The cellular amount of LHCBM6/8 was determined by immunodetection (αL6/8; upper panel) 5 and 8 h following GSNO addition (+) to cultures expressing either wt-NAB1 (wt) or NAB1C226S (C226S) under control of the PSAD promoter. Negative controls (−GSNO) were included to exclude effects unrelated to nitrosative stress. Changes in the level of LHCBM6/8 relative to the t0 level of the wild type (black bars) or C226S (gray bars) were quantified by densitometric scanning (lower panel). Mean values from two biological replicates including two technical replicates are given along with standard deviations (n = 4). C, Effects of Cys-226 nitrosylation on the RNA-binding activity of NAB1 in vivo. Cys nitrosylation was induced by addition of GSNO to liquid cultures expressing wt-NAB1 under control of the PSAD promoter, and samples for the coimmunoprecipitation of LHCBM6-mRNA via NAB1 were taken at indicated time points (x axis). Enrichment factors for LHCBM6-mRNA were determined by comparing the relative LHCBM6 amount in input and coprecipitated samples for each time point by applying quantitative RT-PCR. The GSNO-induced change in LHCBM6-mRNA enrichment during NAB1 immunoprecipitation was calculated by setting the enrichment factor obtained before (t0min) GSNO addition to 100%. Error bars represent standard errors derived from four technical replicates (n = 4).