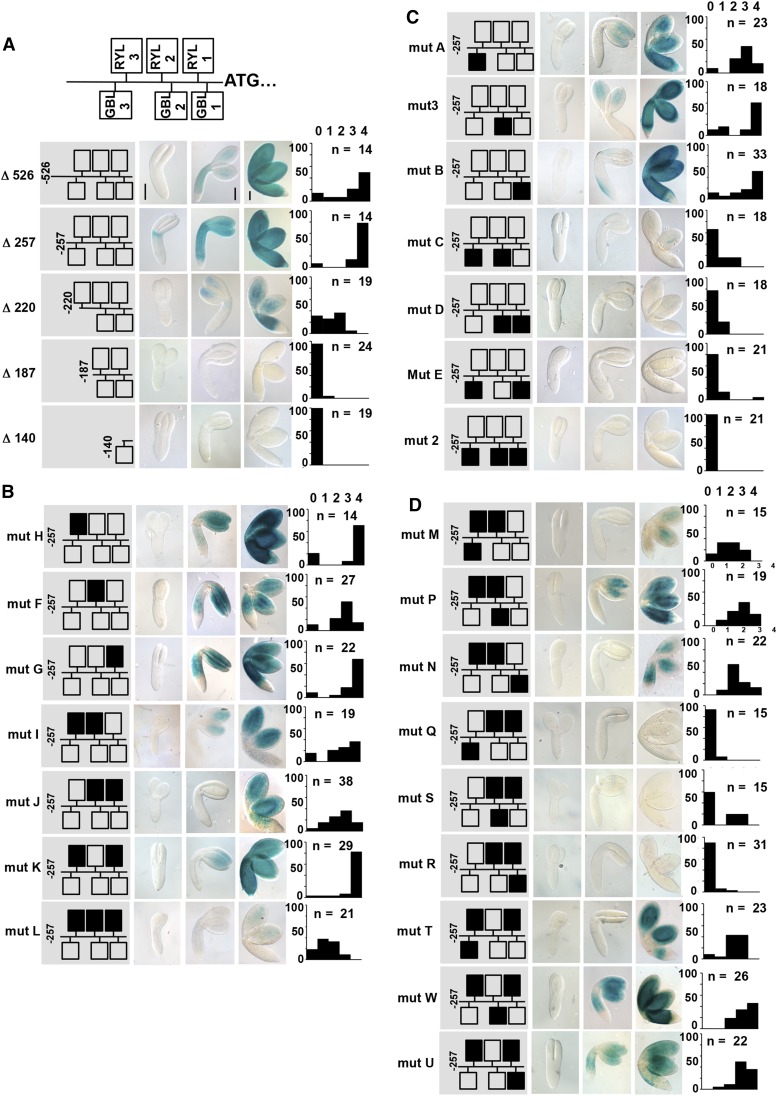
Figure 2.
Functional dissection of the OLE1 promoter in planta. A, At top is a schematic representation of the RYL and GBL elements identified within the OLE1 promoter sequence. A series of 5′ deletions was generated, and translational fusions to the uidA gene were prepared. The corresponding transgenic embryos were assayed for GUS activity at the torpedo, bent-cotyledon, and maturing stages. The length of the promoter tested is indicated at left. B and C, Mutations of the RYL (B) and GBL (C) elements were generated in the context of the 257-bp OLE1 promoter, and translational fusions to the uidA gene were prepared. The corresponding transgenic embryos were assayed for GUS activity. D, Combinations of mutations affecting GBL and RY elements were generated in the context of the 257-bp OLE1 promoter, and translational fusions to the uidA gene were prepared. The corresponding transgenic embryos were assayed for GUS activity. From left to right are the name of the mutagenized promoter under study, a schematic representation of the promoter with mutagenized elements in black, representative photographs of stained embryos at three different stages of the maturation process, and a bar graph showing the partition of staining intensities (from 0 = colorless to 4 = intense staining) among a population of n independent transformants.