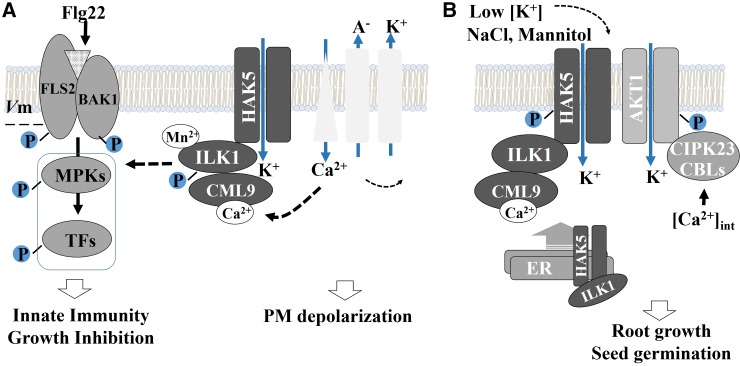
Figure 11.
Preliminary model of ILK1’s roles during stress. A, A model of possible signaling-related functions of ILK1 in PAMP-triggered innate immunity. After flg22 recognition by BAK1-FLS2, Ca2+ influxes trigger anion export, which depolarizes the membrane and induces K+ efflux. Calcium sensors such as CML9 may modulate ILK1 kinase activity that phosphorylates HAK5 or other signaling molecules to activate an unknown signaling pathway. This pathway, which may involve K+-sensing to repress early MPK3/MPK6 signaling, has a net positive effect on plant innate immunity and regulates growth in response to PAMPs. Flg22-triggered membrane depolarization involves rapid activation of several unknown channels, which may include GLR3.3 and are influenced by HAK5 and ILK1 in a kinase-independent manner. B, A model of proposed ILK1 roles in potassium transport for plant responses to abiotic stress. During osmotic stress and limited K+ supply, ILK1 and CML9 promote HAK5 maturation and transport to the membrane. Low intracellular K+ concentrations lead to accumulation of intracellular Ca2+ and signaling through CML9/ILK1 or CBLs/CIPK23, which activate HAK5.