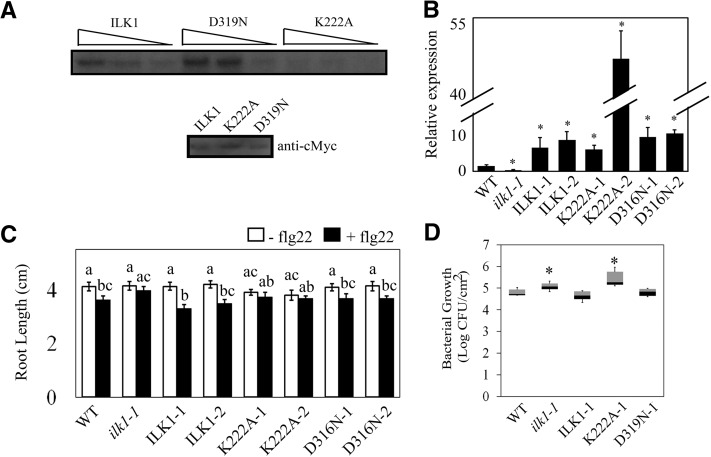
Figure 3.
ILK1 activity is required for the flg22 response and bacterial resistance. A, Autophosphorylation activity of the cMyc-tagged ILK1, ILK1D319N, or ILK1K222A isoforms exposed to 5 mm Mn2+ and visualized by autoradiography. Equal loading of the protein was verified by western blot and decreasing relative concentrations (1, 0.5, and 0.25) of the enzymes were used as indicated by triangles. B, ILK1 gene expression is enhanced in the ilk1-1 lines transformed with clones containing ILK1, or the ILK1D319N (increased kinase activity) or ILK1K222A (decreased kinase activity) isoforms. Two lines for each construct were evaluated (i.e. ILK1-1, ILK1-2). Expression was quantified by qRT PCR in 4–6 biological replicates with two technical replicates and normalized to PP2A gene expression where * indicates significant difference from the wild type, P < 0.05. C, Flg22-induced root growth inhibition is regained in ilk1-1 expressing ILK1 or ILK1D319N but not ILK1K222A. The seedlings were grown for 5 d prior to transfer to liquid MS media containing no flg22 or 100 nm flg22 and primary root length was quantified 10 d after transfer (n = 28–32). The asterisk indicates a significant difference in growth between the flg22-exposed and non-exposed plants within a line, P < 0.05. D, Bacterial growth is enhanced in the ilk1-1 knockdown and ILK1K222A-expressing plants. The number of viable P. syringae pv. tomato ΔhrcQ-U bacteria in rosette leaves were counted 2 d after syringe inoculation (n = 25-36) where * indicates significant difference from the wild type, P < 0.05.