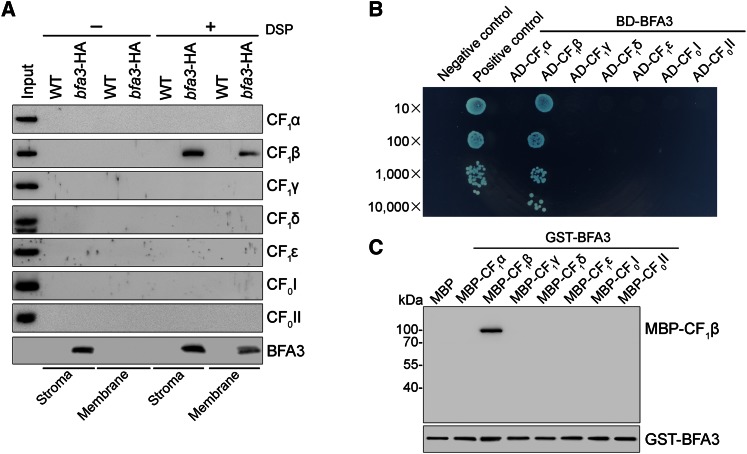
Figure 8.
BFA3 specifically interacts with CF1β. A, Affinity purification of the proteins associated with BFA3. Intact chloroplasts were isolated from leaves of WT and bfa3-HA plants and incubated with (+DSP) or without (-DSP) 2.5 mm DSP on ice for 30 min in the dark. After incubation, chloroplasts were osmotically ruptured and fractionated into stromal and thylakoid fractions. Peripheral thylakoid protein released from thylakoids by 1.2% Triton X-100 and stromal fractions were mixed with anti-HA affinity matrix for immunoprecipitation, respectively. The bound proteins were washed, eluted, and detected by immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. bfa3-HA represents bfa3-1 transformed with WT genomic BFA3 fused to the sequence encoding the HA epitope-tag. Thylakoid proteins corresponding to 0.2 μg chlorophyll were loaded as indicators for antibodies. B, Yeast two-hybrid analysis. BFA3 was fused to the bait vector. Subunits of the CF1 subcomplex as well as soluble parts of CF0I and CF0II were fused to the prey construct. Cotransformation of pGBKT7-53 with pGADT7-T was used as a positive control, whereas cotransformation of pGBK7-Lam with pGADT7-T was used as a negative control. As another negative control (Supplemental Fig. S4) included to rule out self-activation of the prey, pGBKT7 was cotransformed with pGADT7 harboring ATP synthase subunits. AD, GAL4 activation domain; BD, GAL4 DNA-binding domain. C, In vitro pull-down assay. GST-BFA3 fusion was used as bait. MBP-tagged CF1α, CF1β, CF1γ, CF1δ, and CF1ε subunits as well as the MBP-tagged soluble parts of CF0I and CF0II were used as prey. After incubation of bait and prey proteins for 1 h at 4°C, glutathione-agarose beads were added to precipitate the bait and bound prey proteins. The bound proteins were eluted and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against MBP and BFA3.