Fig. 1.
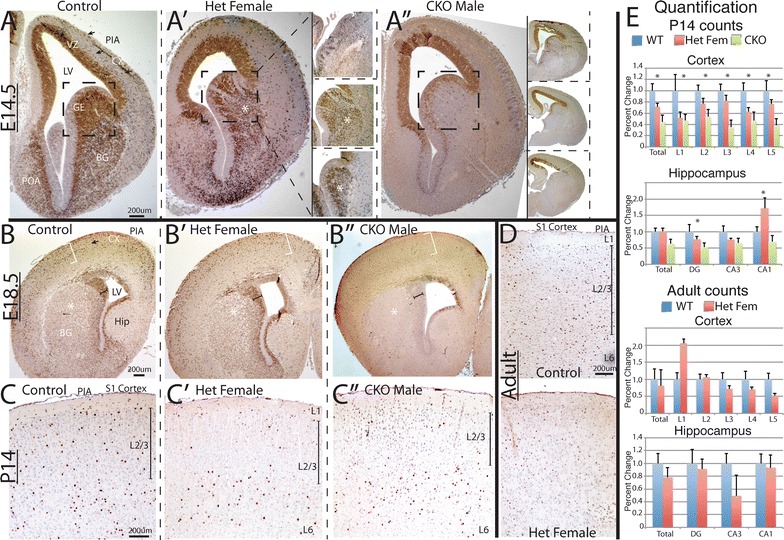
Arx expression across the ages in control and Arx −/x and Arx −/y ;Dlx5/6 CIG mice. A–A″ e14.5 embryos in coronal plane. A control, A′ female het, A″ male CKO. Immunohistochemistry for Arx reveals near complete loss of Arx in the ventral pallium, in both VZ, SVZ and developing basal ganglia (A″), but persistence in the cortical VZ. There is near complete loss of Arx positive cells in the developing cortex as well in the male CKO (A″). Even with loss of Arx, the anatomy of the ventral pallium is unchanged (boxed areas in A″). A′ insets (from area around asterisk in main image) reveals a spectrum of X inactivation patterns and variability of expression of Arx in 4 representative examples of heterozygous females at e14.5. Only the GE is highlighted in each inset. Stripes of clonal expansion of both Arx absence and presence are observed emanating from the VZ. A″ insets—four representative examples demonstrating the variability of loss of Arx in CKO males; from moderate loss (top inset) to complete loss (bottom inset). Arrows in A highlight migrating interneurons. B–B″ Representative e18.5 coronal images. B Control, B′ female het, B″ male CKO. At 18.5 there are many fewer cell in the Arx −/y ;Dlx5/6 CIG than in the wildtype, including the dorsal cortex (white brackets), ventral BG (asterisk) and VZ of GE (capped black line). There are an intermediate number of cells in both locations in the female heterozygous animals (B′). Again note anatomy of developing BG is unchanged in all three genotypes. C–C″ Representative P14 coronal images. C Control, C′ female het, C″ male CKO. Arx staining illustrates that the persistent Arx positive cells in the surviving Arx −/y ;Dlx5/6 CIG mice (C″). In this animal the cells were mostly in the lower layers but there was variability in the 4 mutants so this was not statistically significant. A similar pattern was also found in many of the heterozygous females (C′) whereas the wildtype brains have cells dispersed throughout the cortex (C). D Representative adult coronal images. Upper panel control, lower panel female het. No significant differences are noted. E Quantification of Arx cell numbers in cortex and hippocampus at P14 and in adult animals across all layers and hippocampal regions. Upper panels are counts from P14 animals. Total is the sum of the counts of all layers. L1–L5 are five equally spaced regions that correspond roughly to cortical layers (see “Methods”). Asterisk signifies statistical differences. Lower panels are counts from adult animals. LV lateral ventricle, SVZ subventricular zone, VZ ventricular zone, BG basal ganglia, GE ganglionic eminence, Cx developing cortex. Hip hippocampus. L1 cortical layer 1, L2/3 cortical layers 2 and 3, L6 cortical layer 6
