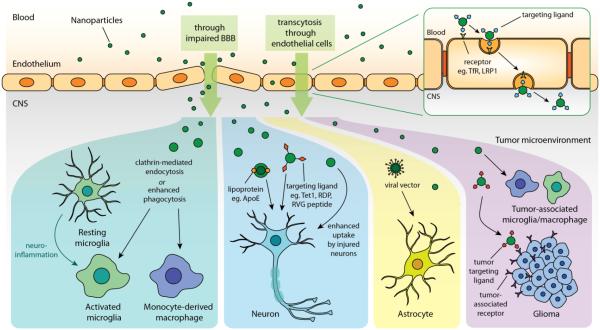
Figure 3. Schematic representation of the strategies for targeted drug delivery to different cell phenotypes in CNS.
First, nanomedicine can either enter CNS through impaired BBB or cross BBB endothelium via receptor-mediated transcytosis when the drug/cargo circulates systematically. Nanomedicine can potentially be uptake by activated microglia, infiltrating macrophage, or tumor-associated microglia/macrophage through clathrin-mediated endocytosis or phagocytosis. The drug/cargo can also possess cell-targeting properties when a targeting moiety is incorporated. Vesicles with lipoprotein ApoE or nanoparticles with ligands (eg. Tet1, RDP, RVG peptides) can be particularly uptake by neurons. Viral vector homing to astrocyte could be an effective cargo to deliver therapeutics. Nanoparticles functionalized with tumor targeting ligand can also be introduced to target glioma with enhanced accumulation.