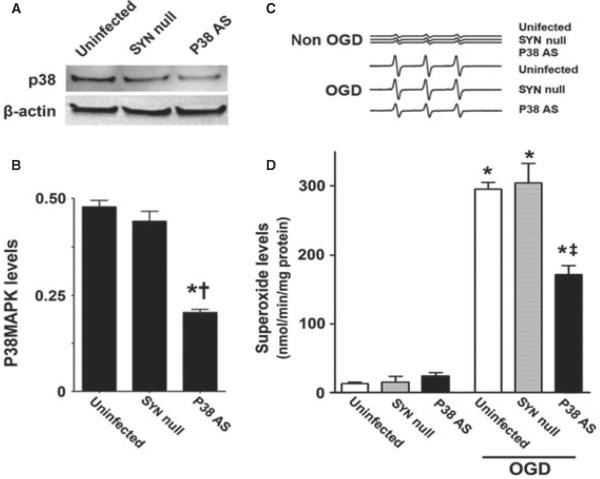
Fig. 7.
Targeted decreases in p38 MAPK expression in neuronal cells attenuate superoxide generation in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Rat hippocampal slice cultures were transduced with either the AAV-SYN-1-p38 MAPK-AS or the AAV-SYN-1null constructs or were untransduced. After 7 days, slices were harvested and subjected to western blot analysis to determine the effects on p38 MAPK protein levels. A representative image is shown (A). The AAV-SYN-1-p38 MAPK-AS construct significantly decreases p38 MAPK levels (B). Slices were also exposed to OGD, harvested at 8 h and then subjected to EPR using the spin-trap compound 1-hydroxy-3-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine.HCl to determine superoxide levels. Representative EPR waveforms are shown (C). Absolute levels of superoxide generation were then determined as nanomols superoxide generated / min per mg protein (D). Values are presented as mean + SE from four independent experiments using 12 pooled slices per experiment. *P < 0.05 vs. uninfected, †P < 0.05 vs. AAV-SYN-1null-exposed slices, ‡P < 0.05 vs. OGD-exposed untransduced slices.