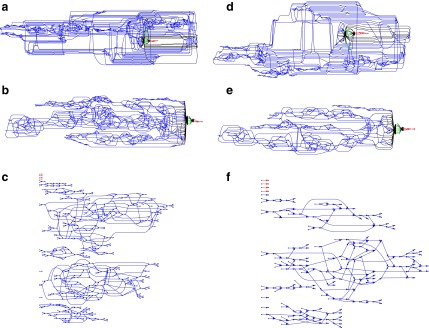
FIG. 2.
The canonical antibody graph for different values of 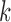 (arcs corresponding to the V, D, and J gene segments are colored blue, green, and red, respectively) constructed for all alleles (left) and all consensus gene-segments (right). All nonbranching paths are collapsed to a single arc, and at each junction, a dummy node is created to connect V gene segments to D gene segments, and D gene segments to J gene segments; these arcs are colored black. These graphs are constructed with
(arcs corresponding to the V, D, and J gene segments are colored blue, green, and red, respectively) constructed for all alleles (left) and all consensus gene-segments (right). All nonbranching paths are collapsed to a single arc, and at each junction, a dummy node is created to connect V gene segments to D gene segments, and D gene segments to J gene segments; these arcs are colored black. These graphs are constructed with 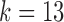 (a and d),
(a and d),  (b and e), and
(b and e), and 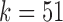 (c and f). Panel (b) shows V, D, and J gene segments completely separated, while (a) shows considerably more sharing of arcs in the V segments, and some shared in the D gene segments. Increasing the value of
(c and f). Panel (b) shows V, D, and J gene segments completely separated, while (a) shows considerably more sharing of arcs in the V segments, and some shared in the D gene segments. Increasing the value of 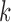 (c) greatly simplifies the relationship among V gene segments. This is not a feasible parameter for our purposes (as no D segments are captured) but does show the complexity of V gene segments. In the case of
(c) greatly simplifies the relationship among V gene segments. This is not a feasible parameter for our purposes (as no D segments are captured) but does show the complexity of V gene segments. In the case of 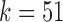 , the graph becomes disconnected (and green edges disappear), since it exceeds the length of the longest D gene segment.
, the graph becomes disconnected (and green edges disappear), since it exceeds the length of the longest D gene segment.