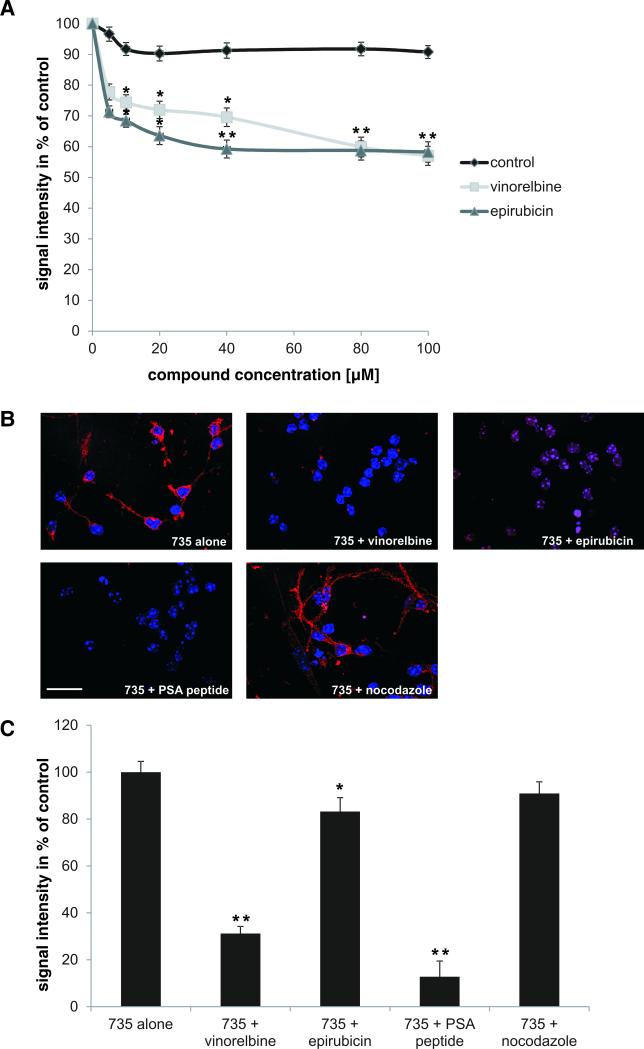
Fig. 2. Vinorelbine and epirubicin compete with colominic acid for binding to the PSA-specific antibody 735.
(A) Colominic acid coupled to catalase was immobilized in 384-wells and incubated with antibody 735 in the presence of vinorelbine (light gray line) or epirubicin (dark grey line) at 100 nM – 100 μM concentrations (means ± SEM). The signal from antibody binding to colominic acid was set to 100%. Vinorelbine and epirubicin compete with colominic acid for binding to antibody 735 in a concentration dependent manner reaching a maximal effect at 40 to 80 μM concentrations. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.005; two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey's post hoc testing. (B) Representative images of cerebellar neurons stained with PSA antibody mAb 735 (Cy3; red) alone or in the presence of vinorelbine or epirubicin, PSA peptide (positive control) or nocodazole (negative control). Nuclei are shown in blue. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) Histogram showing the quantification of immunostainings from 50 cells (means + SEM). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA).