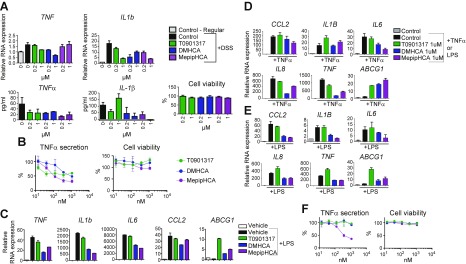
Figure 2.
Sterol-based LXR agonists reduce inflammation in mouse LPMCs, mouse peritoneal cells, human colonic epithelial cells, and human PBMCs. A) LPMCs were isolated from mice treated with or without DSS water. Freshly isolated LPMCs were treated with 1 μM LXR agonists for 16 h before being collected for RNA expression analysis (upper panel), cytokine secretion analysis, and cell viability by CellTiter Glo assay (lower panel). B) Mouse peritoneal cells were treated with LXR agonists of different concentrations for 6 h before stimulation with LPS for 16 h, followed by HTRF TNF-α secretion assay. C) Mouse peritoneal cells were treated with 1 μM LXR agonists for 6 h before LPS stimulation for 1 h for gene expression analysis. D, E) SW480 cells were pretreated with control or compounds at concentrations as indicated for 16 h, before 10 ng/ml TNF-α (D) or 100 ng/ml LPS (E) stimulation. After 1 h, cells were collected and RNA was isolated. RT-qPCR was performed to determine the gene expression of CCL2, IL1B, IL6, IL8, TNF-α, ABCG1. F) Primary human PBMCs were treated with different LXR agonists for 6 h followed by LPS stimulation for 16 h. TNF-α secretion was assessed by HTRF assay and cell viability by CellTiter Glo assay. Results are presented as means ± sd.