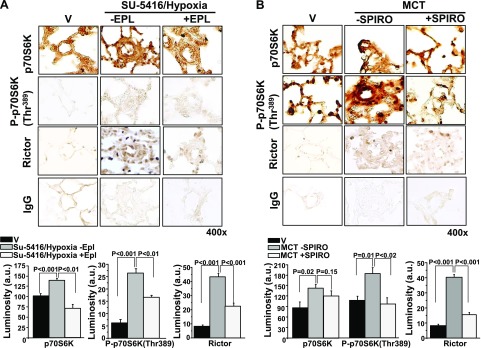
Figure 2.
The effect of MR receptor antagonism on p70S6K expression in 2 models of experimental PAH. A) Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were injected with SU-5416 and exposed to chronic hypoxia for 21 d. Immediately after exposure to hypoxia, rats were randomly assigned to receive standard chow or eplerenone (EPL; 0.6 gm/1 gm chow) until completion of the study (n = 4–6 rats/condition). B) In a second model, SD rats were randomly assigned to receive vehicle control (V) or spironolactone (SPIRO; 25 mg/kg/d) immediately after the i.p. administration of V or MCT (50 mg/kg) (n = 3 rats/condition). Immunohistochemistry was performed on distal pulmonary arterioles measuring 20–50 μm in diameter to assess pulmonary arteriole levels of p70S6K or P-p70S6K(Thr389), which is the activated form of p70S6K associated with increased ribosomal activity and cell growth. The effect of MR inhibition on expression levels of Rictor, which is the active subunit of mTORC2, was also assessed. IgG served as negative control. Data are presented as mean ± sem. All images were obtained at 400× magnification. Representative micrographs are shown.