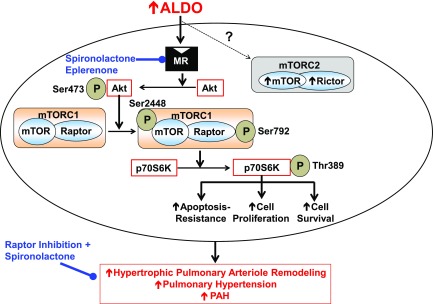
Figure 9.
Summary of aldosterone-Raptor signaling in the development of pulmonary arteriole remodeling and pulmonary hypertension in PAH. Elevated circulating levels of aldosterone (ALDO) in PAH stimulate the MR to induce the activation of p70S6K via up-regulation of the Akt/mTOR/Raptor axis in PASMCs. Aldosterone-p70S6K signaling promotes apoptosis resistance, cellular proliferation, and increased cell survival in vitro, which is associated with concentric hypertrophic remodeling of distal pulmonary arterioles and pulmonary hypertension in PAH in vivo. In turn, MR inhibition with spironolactone or eplerenone prevents the adverse effects of aldosterone-Raptor in vitro, whereas molecular inhibition of Raptor, in combination with spironolactone, was more effective than Raptor inhibition alone for reversing or preventing experimental PAH.