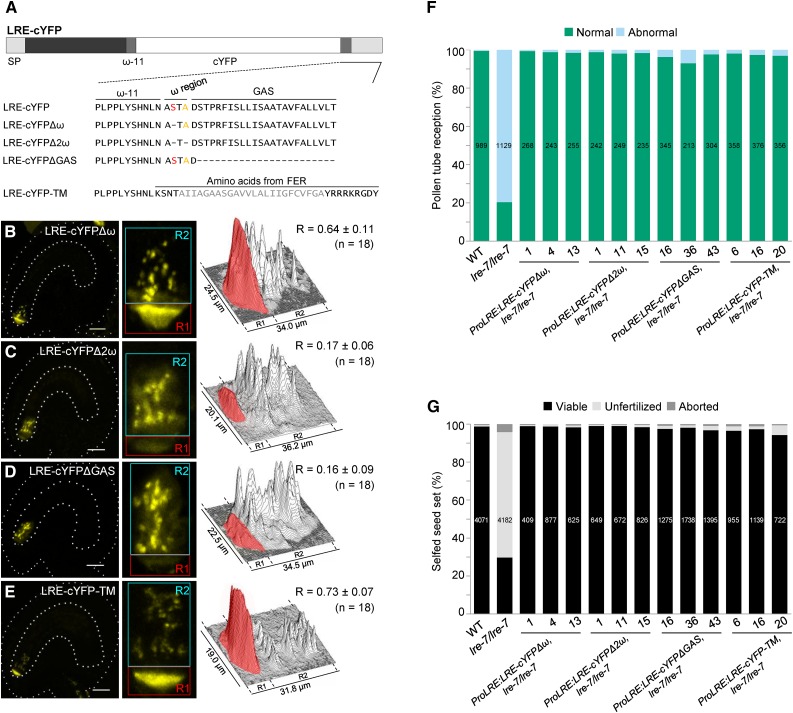
Figure 3.
Predicted GPI Anchor Addition Domains Are Necessary for LRE Localization in the Filiform Apparatus but Not Its Function in Pollen Tube Reception.
(A) Diagram of the LRE-cYFP protein. Wild-type or altered amino acid sequence on either side of the predicted ω amino acid in each construct is indicated below the diagram. In LRE, the best predicted ω and a cryptic ω site are labeled in red and orange, respectively. Each dash in the protein sequence represents a deletion of the corresponding amino acid in wild-type LRE protein sequence. GAS, GPI attachment signal (lighter gray rectangle). In LRE-cYFP-TM, predicted transmembrane region of FER is in gray.
(B) to (E) Localization of LRE-cYFPΔω (B), LRE-cYFPΔ2ω (C), LRE-cYFPΔGAS (D), and LRE-cYFP-TM (E) in the synergids of the female gametophyte. Left panels, representative image showing the localization of each fusion protein; middle panels, close-up view of the micropylar region in corresponding left panel images; right panels, surface plots showing quantification of cYFP signal in the region of filiform apparatus (red box) and the remainder of the synergids (cyan box) as in Figure 2F. Bar = 20 µm.
(F) and (G) Constructs with altered GPI addition domains fully complement pollen tube reception defect (F) and the reduced seed set defect (G) in lre-7/lre-7 plants. Total number of ovules (F) and seeds (G) analyzed are in the center of each column. Number below each column, the three lines used that are single insertion and homozygous for the indicated transgenes in the lre-7/lre-7 background.