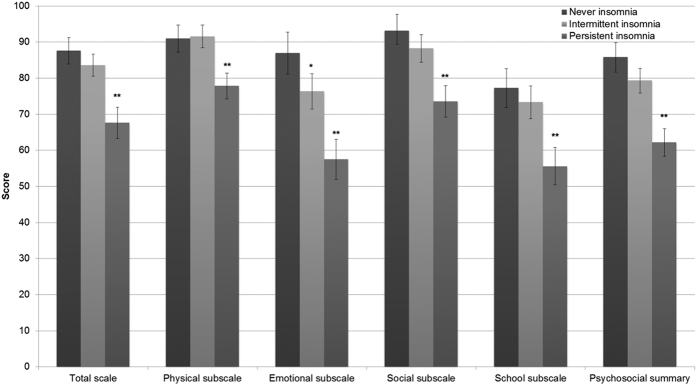
Figure 2. PedsQL Scores in participants with nocturnal symptom-based insomnia.
The presence of insomnia is associated with decreased HRQOL across multiple domains of the PedsQL. This effect was greater in in the total, emotional, social and psychosocial scores of individuals with persistent insomnia. *Significantly different (p < 0.05) from no insomnia, **significantly different from intermittent insomnia. Insomnia was defined as presence of at least one of the following symptoms: trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early in the morning. PedsQL scores were adjusted for age, gender, ethnicity, family income, parent education, reported oat least one of the following daytime symptoms bstructive sleep apnea and use of psychiatric medication.