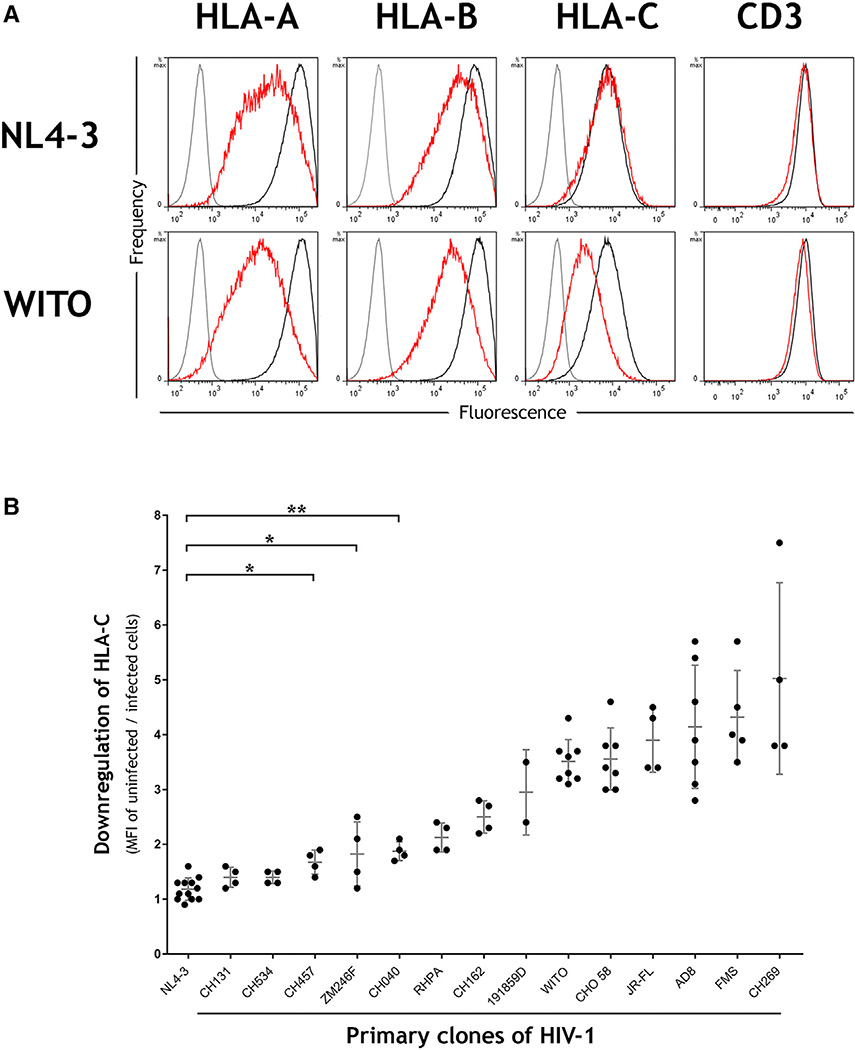
Figure 1. HLA-C Is Downregulated by Most Primary Clones of HIV-1 in Contrast to the Laboratory-Adapted Clone NL4-3.
(A) Primary CD4+ cells were infected in vitro with the HIV-1 molecular clones NL4-3 or WITO. Flow cytometry staining of HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, or CD3 is shown for infected (red) or uninfected cells (black) and an isotype control (gray). Infected cells within cultures were discriminated by co-staining the viral protein Gag, and CD4 cell donors were homozygous for the A*02:01, B*44:02, C*0501 haplotype.
(B) Downregulation of HLA-C is a common feature among primary clones of HIV-1. Primary CD4+ cells were infected in vitro with a panel of HIV-1 infectious molecular clones (x axis), and HLA-C downregulation was determined by flow cytometry (y axis). MFI indicates median fluorescence intensity. Plotted points represent independent infections and include donors with different HLA types. Error bars show ± 1 SD. Statistical comparisons used unpaired t tests where *p < 0.005 and **p < 0.0001, and each virus to the right of CH040 also differs from NL4-3 with p < 0.0001.