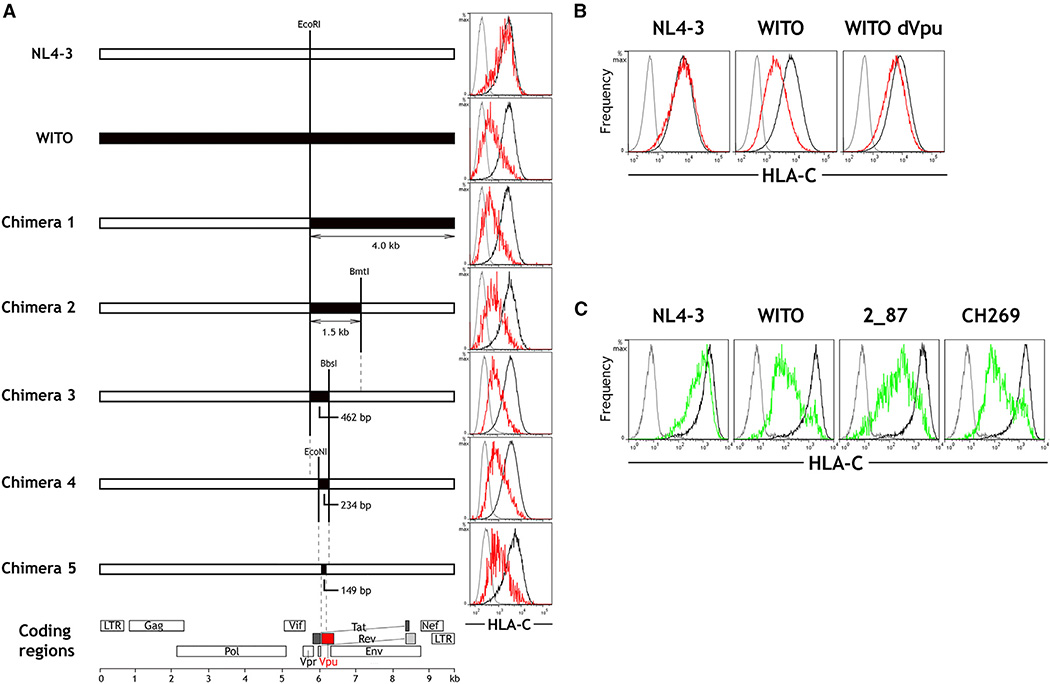
Figure 2. The HIV-1 Protein Vpu Is Responsible for Downregulation of HLA-C.
(A) Full-length HIV-1 genomes were constructed comprising sequences from NL4-3 (white) and WITO (black). Flow cytometry plots show staining of isotype control (gray) and HLA-C on HIV+ (red) or HIV− (black) HeLa cells after transfection with the corresponding HIV-1 constructs and HIV+/− cell discrimination by staining viral Gag. In the final chimera 5, the 149-bp region from WITO encodes part of Vpu.
(B) Primary CD4+ cells were infected in vitro with molecular clones of NL4-3, WITO, or WITO with the Vpu initiation site ablated. Flow cytometry staining for HLA-C on infected (red) and uninfected cells (black) is shown compared with an isotype control (gray), where HIV+ cells were discriminated by staining viral Gag.
(C) Vpu genes cloned from NL4-3 or the primary HIV-1 subtype B viruses WITO and 2_87 and the primary subtype C virus CH269 were expressed in HeLa cells. Flow cytometry staining for HLA-C on Vpu+ (green) or Vpu− (black) cells discriminated by co-transfection with a GFP-expressing plasmid is shown compared with an isotype control (gray) and is representative of three independent experiments.
See also Figures S3 and S4.