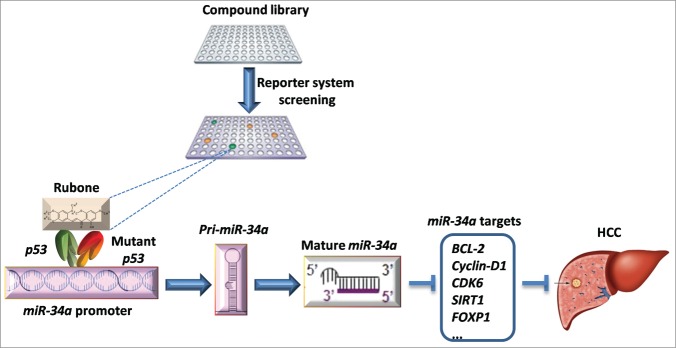
Figure 1.
Screening of p53-dependent miR-34a modulators that inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma. Schematic representation of screening for miR-34a modulators and the identification of one compound, called Rubone, that increased both wild-type and mutant p53 occupancy on the miR-34a promoter. Rubone increased miR-34a expression and subsequently downregulated the expression of miR-34a targets such as CYCLIN D1, BCL-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2), CDK6 (cyclin-dependent kinase 6), SIRT1 (Sirtuin 1), and FOXP1 (Forkhead box protein P1), ultimately inhibiting HCC growth.