Figure 1.
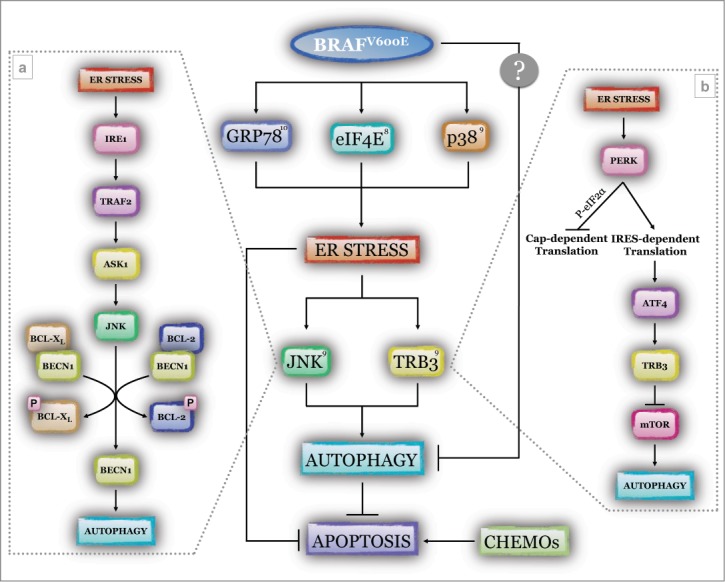
ER stress induced by oncogenic BRAF and modulation of basal autophagy in melanoma. Oncogenic serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf carrying the V>E mutation (BRAFV600E) stimulates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress through the involvement of at least 3 major factors, glucose-regulated protein 78kDa (GRP78), eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), and mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 (p38). Through direct interaction with GRP78, mutant BRAF relieves its inhibitory activity toward the 3 stress sensors, activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE1), and double-stranded RNA activated protein kinase (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK),10 and thus inducing the unfolded protein response (UPR). Stimulation of the activity of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK/ERK) signaling pathway drives phosphorylation of the translational factor eIF4E, hyperstimulating the translational signaling pathway and resulting in protein accumulation in the ER compartment;8 activation of p38 (through protein phosphorylation) drives the activation of the above mentioned ER stress sensors, resulting in UPR.9 ER stress in turn enhances the activity of the autophagic process through the PERK/activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4)/mammalian homolog of Drosophila tribbles (TRB3) and the IRE1/TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2)/apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) axes. In the first signaling pathway (B), active PERK phosphorylates the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α), a factor controlling the initiation of cap-dependent protein translation, thus stimulating the IRES-dependent translational process. This favors accumulation of the transcription factor ATF4 that in turn stimulates the synthesis of TRB3, which induces the autophagic process through inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activity. In parallel (A), active IRE1 recruits and activates the cytosolic kinase ASK1 through the adapter molecule TRAF2, which in turn activates JNK. The latter phosphorylates the BECLIN 1 (BECN1) inhibitory partners B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) and BCL2-like 1 isoform 1 (BCL-XL), resulting in BECN1 release and subsequent autophagy induction. Therefore, mutant BRAF-mediated dysregulation of prosurvival pathways such as ER stress and autophagy sustains tumor development and progression, and desensitizes cancer cells to therapy-induced apoptosis (CHEMOs).
