Figure 1.
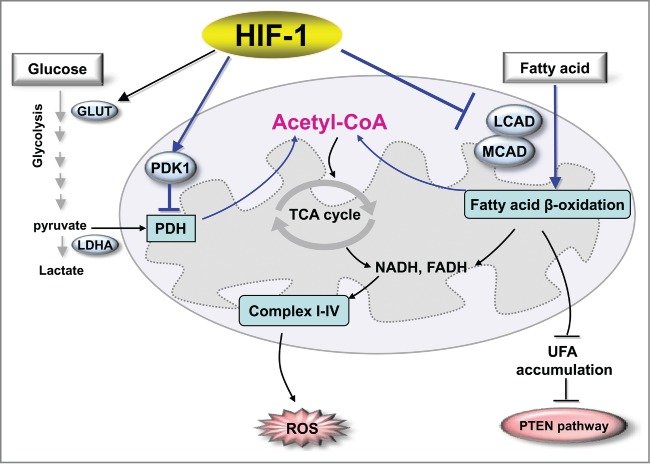
HIF-1 regulates the metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells. For glucose metabolism, HIF-1 enhances glycolytic metabolism by upregulating glucose transporters and glycolytic enzymes to enhance the flux of glycolysis, by inducing PDK1 to block the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, and by activating LDHA to convert pyruvate to lactate. In the regulation of lipid metabolism, HIF-1 inhibits catabolism of fatty acids by repressing LCAD and MCAD, leading to suppression of ROS levels and accumulation of fatty acid that blunts PTEN expression and enhances cancer cell proliferation. Abbreviations: HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; GLUT, glucose transporter; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A; PDK1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme 1; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; MCAD, medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; LCAD, long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, UFA, unsaturated fatty acid; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
