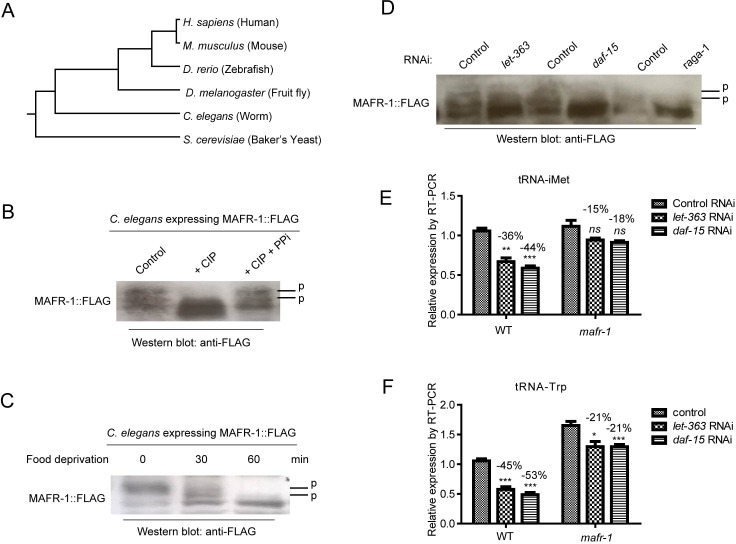
Figure 2. MAFR-1 is conserved and regulated similarly by mTOR pathway.
A. MAFR-1 is conserved in evolution. Phylogenic analysis was based on protein sequence of Maf1 homologs in indicated species. B. MAFR-1 is a phosphoprotein similar to yeast and human Maf1. Protein lysate from young adult worms expressing FLAG-tagged MAFR-1 was treated with calf intestine phosphatase (CIP) only or together with phosphatase inhibitor (PPi), then western blotted for MAFR-1 using FLAG antibody. Phosphorylated species (P) migrated slower, which collapsed after CIP treatment but protected by PPi. C. MAFR-1 phosphorylation is decreased by starvation similarly to yeast and human Maf1. Young adult worms expressing MAFR-1::FLAG were deprived from food for 30 min or 60 min. MAFR-1 phosphorylation was analyzed by western blot. D. MAFR-1 phosphorylation is sensitive to mTOR inhibition. mTOR is inhibited by RNAi knocking down of let-363, which encodes the mTOR kinase, and daf-15, which encodes the Raptor homolog. E. tRNA of the initial Methionine is decreased by mTOR inhibition but alleviated by mafr-1 deletion. mTOR is inhibited by RNAi knocking down of let-363 and daf-15. tRNA levels were detected by RT-qPCR. F. tRNA of the Tryptophan is decreased by mTOR inhibition but alleviated by mafr-1 deletion. Experiment was conducted as in E.