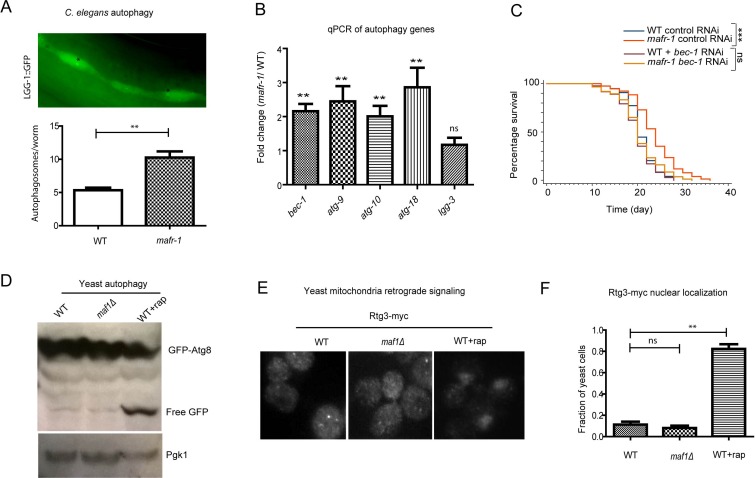
Figure 5. Autophagy is induced in worms with MAFR-1 loss.
A. Autophagosome levels were higher in mafr-1 mutant worms. Autophagosomes in the seam cells of adult animals can be observed by LGG-1::GFP (upper panel). Lower panel shows the quantification. Error bars indicate the SEM of 3 separate experimental results. Student's t-test: **p < 0.001. B. Autophagy genes are induced in mafr-1 mutant worms. Relative expression of several key genes involved in autophagy was measured by qPCR. Error bars indicate the SEM of 3 separate experiments. Student's t-test compared mafr-1(−) with WT: **p < 0.001. C. The extended lifespan of mafr-1 worms is dependent on autophagy. bec-1 is required for autophagy induction and was knocked down by feeding RNAi. Chi-square test: ***p < 0.0001, ns, not significant. D. Autophagy is not induced by loss of Maf1 in yeast. Indicated cells expressing GFP-Atg8 were cultured to log phase (OD600 = 0.6) and WT cells were treated with rapamycin as positive control. Cells were lysed and western blotted to detect the free GFP. The level of free GFP is a sensitive indicator of autophagic activity. Pgk-1 was used as a protein loading control. E. Mitochondrial stress signaling is not induced in yeast lacking Maf1. The retrograde signaling senses mitochondrial stress, causing nuclear localization of Rtg3, as shown by rapamycin treatment. Log phase cells expressing Rtg3-myc were fixed and immuno-stained with anti-myc antibody. F. Quantification of yeast cells with nuclear Rtg3. Error bars show the SEM of 3 separate experiments. Student's t-test: **p < 0.001, ns, not significant.