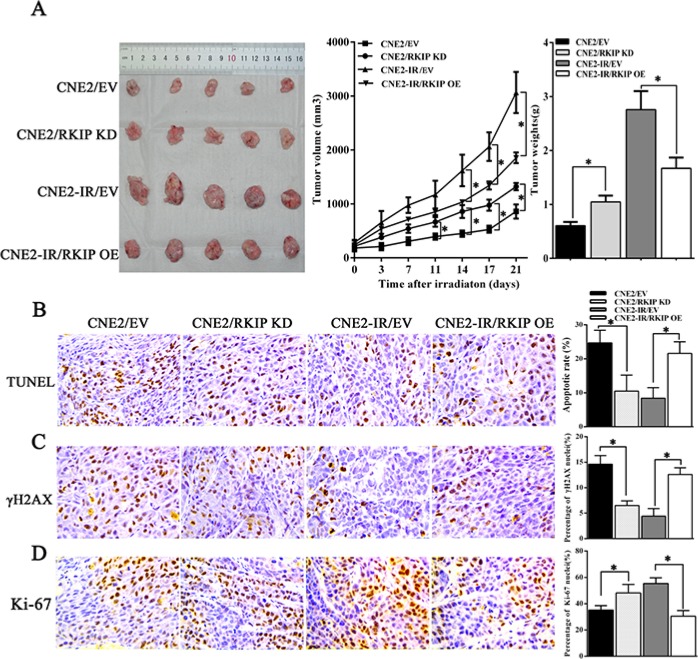
Figure 4. RKIP reduction increases NPC cell radioresistance in vivo.
(A) the growth and weight of tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after 8Gy irradiation. (left) 3 weeks after irradiation, the mice were killed, and the tumors were photographed; (middle) the growth curves of the tumors after irradiation (n = 5 each group) at the sacrifice with respect to the first measurements; (right) the average weights of the tumors after irradiation (n = 5 each group) at the sacrifice. (B) (left) a representative image of TUNEL detection of apoptotic cells in the tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after irradiation; (right) a histogram shows percentages of apoptotic cells in the tumors (n = 5 each group). (C) (left) a representative image of immunohistochemical staining of γH2AX in the tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after irradiation; (right) a histogram shows percentages of γ-H2AX positive cells in the tumors (n = 5 each group). (D) (left) a representative image of immunohistochemical staining of Ki-67 in the tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after irradiation; (right) a histogram shows percentages of Ki-67 positive cells in the tumors (n = 5 each group). Means, SDs, and statistical significance are denoted; *P < 0.01. Original magnification, ×400. OE, overexpression; KD, knockdown; EV, empty vector.